Gen. Chance Saltzman has assumed the responsibility of the U.S. Space Force by accepting the flag from Secretary of the Air Force Frank Kendall at the transition ceremony for the Chief of Space Operations at Joint Base Andrews, Maryland.
Pledging to build on the Space Force’s achievements while also infusing the nascent service with new approaches, Gen. B. Chance Saltzman was officially installed November 2 as Chief of Space Operations, the service’s highest-ranking military post and only the second person to hold the position in the Space Force’s history.
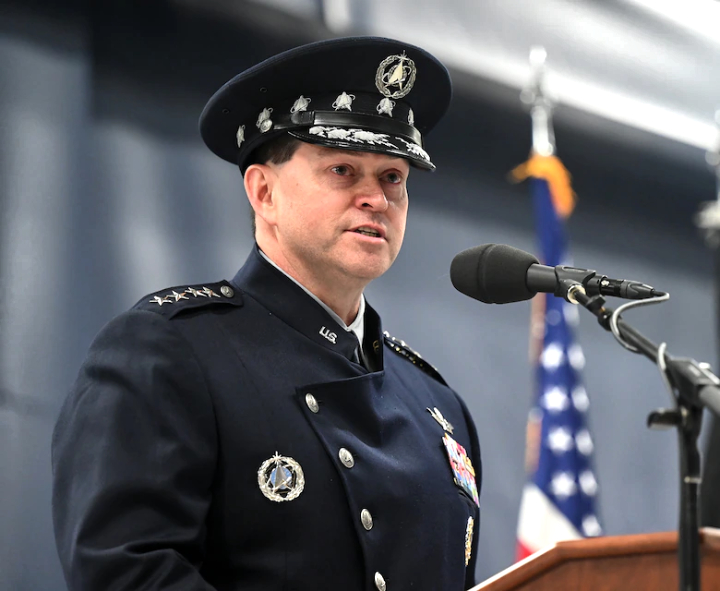

Saltzman praised Raymond for doing “the heavy lifting to establish the Space Force,” for being a mentor and for setting the Space Force on a path on which Saltzman can build. He also thanked his wife Jennifer, his two children and a long list of other, unnamed friends and colleagues who he said comprised the “bedrock of support” across his career.
In addition to Raymond, Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, Gen. Mark Milley, Department of the Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall, took part in the ceremony. As CSO, Saltzman will join Milley and as a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff.

In remarks during a solemn “Change of Responsibility” ceremony in which he was elevated to the job from retiring CSO, Gen. John “Jay” Raymond, Saltzman promised to “work relentlessly to make the Space Force the combat-ready force that our nation needs” while acknowledging it “will not be an easy or short-lived task. You have my commitment that I will work relentlessly to make the Space Force the combat-ready force that our nation needs, so get ready because I’m going to need your best as well,” he added, referring to the cadre of nearly 15,000 Guardians and civilians who currently comprise the Space Force. Saltzman said he will rely on them to continue building the Space Force and ensuring that it succeeds. “My goal will be to provide you the resources, tools, training and experiences you need to unlock your massive potential.”
In his remarks, Austin praised Raymond’s service and his work guiding the Space Force since its creation. He called Saltzman a worthy and capable successor. “There is no one better to take the helm than Gen. Chance Saltzman. For the past two years he’s helped this new service get off the ground as a Deputy Chief of Space Operations. So we’re lucky to have Gen. Saltzman take the colors today. The world is becoming increasingly dangerous and preserving U.S. national security interests in space is growing harder every day. Without the space capabilities you are designing, building, protecting, and operating, the Joint Force will not be capable of accomplishing its missions. A resilient, ready, and combat-credible Space Force is indispensable to deterrence today, tomorrow, and every day after that. In the worst case, if deterrence fails, the Space Force will be an indispensable component of our joint force at war.”

Commissioned in 1991 after graduating from Boston University, he has deep operational experience with missile and space systems as a Minuteman III launch officer and as a satellite operator for the National Reconnaissance Office. He also served as the first Chief of Combat Plans for the Joint Space Operations Center, and later, as Chief of Combat Operations.
Despite its small size compared to the other military services, the Space Force’s strategic importance is beyond dispute. Saltzman pledged to build on Raymond’s accomplishments. “The inspired work that General Raymond started has set us on a path,” Saltzman told the Senate Armed Services Committee on September 13 during his confirmation hearing. “It is a path towards advanced capabilities, modern, resilient architectures, and innovative approaches to meet our service missions.”
Saltzman inherits a Space Force as it continues its transition from the early planning and organizational phases required to form the first new branch of the military since 1947 to one that focuses more on the Department of the Air Force’s operational imperatives.
There are now 72 countries actively operating in space. That number is growing as the cost of launching vehicles into space is falling to the point that more nations, along with many commercial enterprises, are jumping in. As congestion in space increases, so too are the intentions for being there. All of that is raising the stakes for being able to operate freely and without threat in space.

Gen. Chance Saltzman relieved Gen. John W. “Jay” Raymond as the second CSO, the senior uniformed officer heading the Space Force. (U.S. Air Force photo by Andy Morataya) Chief of Space Operations Gen. Chance Saltzman speaks at the transition ceremony for the chief of space operations at Joint Base Andrews, Md., Nov. 2, 2022. Saltzman relieved Gen. John W. “Jay” Raymond as the second CSO, the senior uniformed officer heading the Space Force. (U.S. Air Force photo by Andy Morataya)
Chief of Space Operations Gen. Chance Saltzman greets former Secretary of the Air Force James Roche during the transition ceremony for the chief of space operations at Joint Base Andrews, Md., Nov. 2, 2022. Saltzman relieved Gen. John W. “Jay” Raymond as the second CSO, the senior uniformed officer heading the U.S. Space Force. (U.S. Air Force photo by Staff Sgt. Nick Z. Erwin)
Secretary of Defense Lloyd Austin III (left) and Secretary of the Air Force Frank Kendall in the background, Chief of Space Operations Gen. Chance Saltzman renders a salute during his transition ceremony at Joint Base Andrews, Md., Nov. 2, 2022. Gen. Chance Saltzman relieved Gen. John W. “Jay” Raymond as the second CSO, the senior uniformed officer heading the Space Force. (U.S. Air Force photo by Andy Morataya)
Guests salute for the national anthem during the transition ceremony for the chief of space operations at Joint Base Andrews, Md., Nov. 2, 2022. Gen. Chance Saltzman relieved Gen. John W. “Jay” Raymond as the second CSO, the senior uniformed officer heading the Space Force. (U.S. Air Force photo by Eric Dietrich)
Gen. Chance Saltzman (right) assumes command of the Space Force during a transition ceremony for the Chief of Space Operations at Joint Base Andrews, Md., Nov. 2, 2022. Gen. Chance Saltzman relieved Gen. John W. “Jay” Raymond (center) as the second CSO, the senior uniformed officer heading the Space Force. (U.S. Air Force photo by Wayne A. Clark)
Milley used his remarks to highlight Raymond’s service, to thank him for is 38-year career and occasionally poke good-natured fun at him. Turning serious, however, Milley said Raymond “paved the way and is very much a pioneer” in the United States’ journey into space.
Space is now considered a new and indisputable “warfighting domain” which is why the United States – primarily through the Space Force – along with and its allies are focusing heavily on space and adapting to the new conditions. Militarily space has never been more essential since “space power” provides a series of foundational capabilities upon which our joint forces depend.
It wasn’t long ago when space was an exclusive club, limited almost entirely to the United States and Russia (and before that, the Soviet Union). With only two “players” roaming the vast reaches of space it was considered a challenging but peaceful environment.
Article by Charles Pope, Secretary of the Air Force Public Affairs