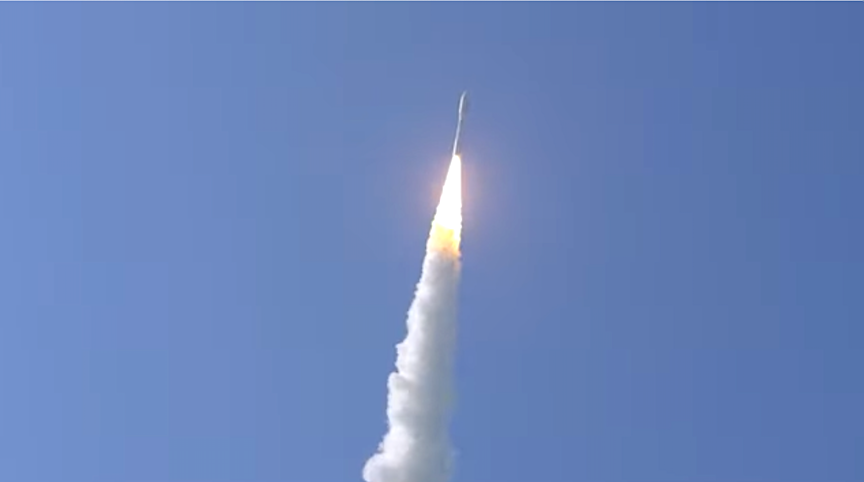
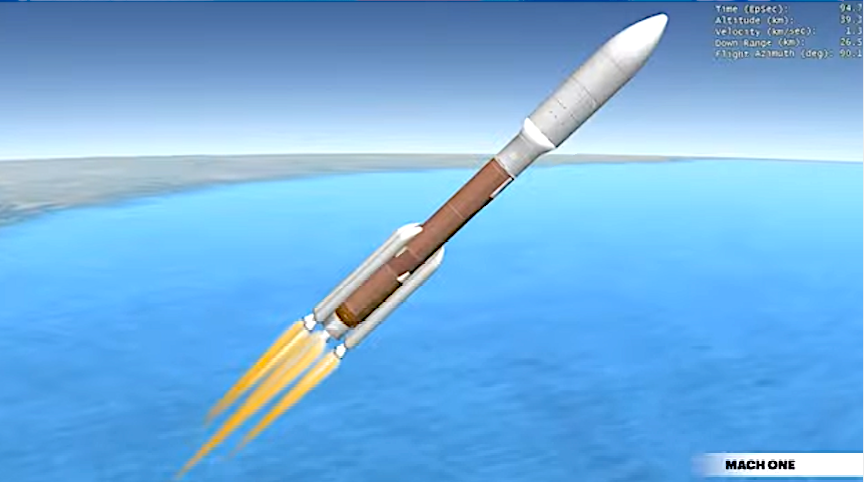
UPDATE: SpaceX successfully launched at 11:22 pm 22 Starlink satellites to low-Earth orbit from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.

This is the seventh flight for the first stage booster supporting this mission, which previously launched Crew-5, GPS III Space Vehicle 06, Inmarsat I6-F2, CRS-28, Intelsat G-37, and one Starlink mission. Following stage separation, the first stage landed in the fog on the A Shortfall of Gravitas droneship, stationed in the Atlantic Ocean.

Despite weather conditions in Florida, SpaceX is targeting Thursday, August 31 at 10:21 p.m. ET (02:21 UTC on September 1) for a Falcon 9 launch of 22 Starlink satellites to low-Earth orbit from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
If needed, additional launch opportunities are available at 11:12 p.m. ET (03:12 UTC on September 1) and 11:29 p.m. ET (03:29 UTC on September 1). Six backup opportunities are also currently available on Friday, September 1 from 7:25 p.m. ET (23:25 UTC) until 10:56 p.m. ET (02:56 UTC on September 2).
This is the seventh flight for the first stage booster supporting this mission, which previously launched Crew-5, GPS III Space Vehicle 06, Inmarsat I6-F2, CRS-28, Intelsat G-37, and one Starlink mission. Following stage separation, the first stage will land on the A Shortfall of Gravitas droneship, which will be stationed in the Atlantic Ocean.
Starlink is available for residential, business, roam, mobility, marine and aviation purposes and more.
A live webcast of this mission will begin about five minutes prior to liftoff.