Rocket Lab USA, Inc. (Nasdaq: RKLB) has been selected to provide hypersonic test launch capability via the company’s HASTE launch vehicle, engineering expertise, and other services through its participation in two, multi-billion dollar government development programs for the United States and the United Kingdom.


Rocket Lab has been selected by the U.S. Air Force to participate within its Enterprise-Wide Agile Acquisition Contract (EWAAC), a $46 billion, indefinite delivery-indefinite quantity (IDIQ) contract designed for the rapid acquisition of innovative technologies, engineering services, and technical solutions that develops the Air Force’s new capabilities. The program has a contracting period through to 2031 and is designed to be broad in scope, flexible in funding, and agile for maximum use to enable the Air Force to quicky procure services and technologies across various domains.
Further, Rocket Lab has also been selected by the United Kingdom’s Ministry of Defence (UK MOD) for its Hypersonic Technologies & Capability Development Framework (HTCDF), a ~$1.3 billion (£1 billion) framework to rapidly develop advanced hypersonic capabilities for the United Kingdom. As a newly-selected supplier to the HTCDF, Rocket Lab is now eligible to bid to provide services, technologies, and testing capabilities that support the UK’s development of sovereign hypersonic technology.
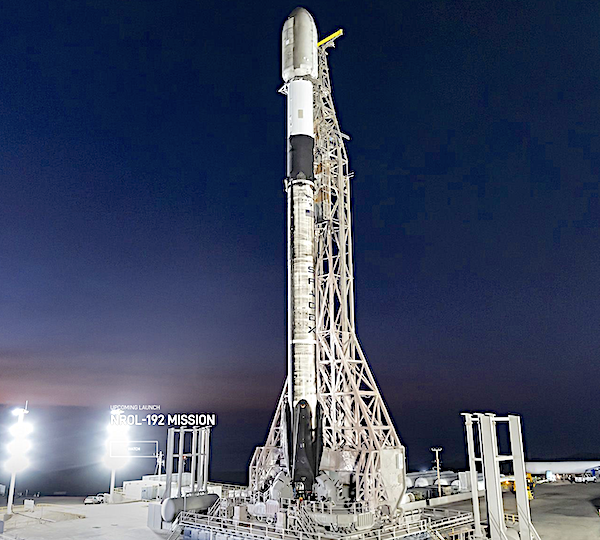
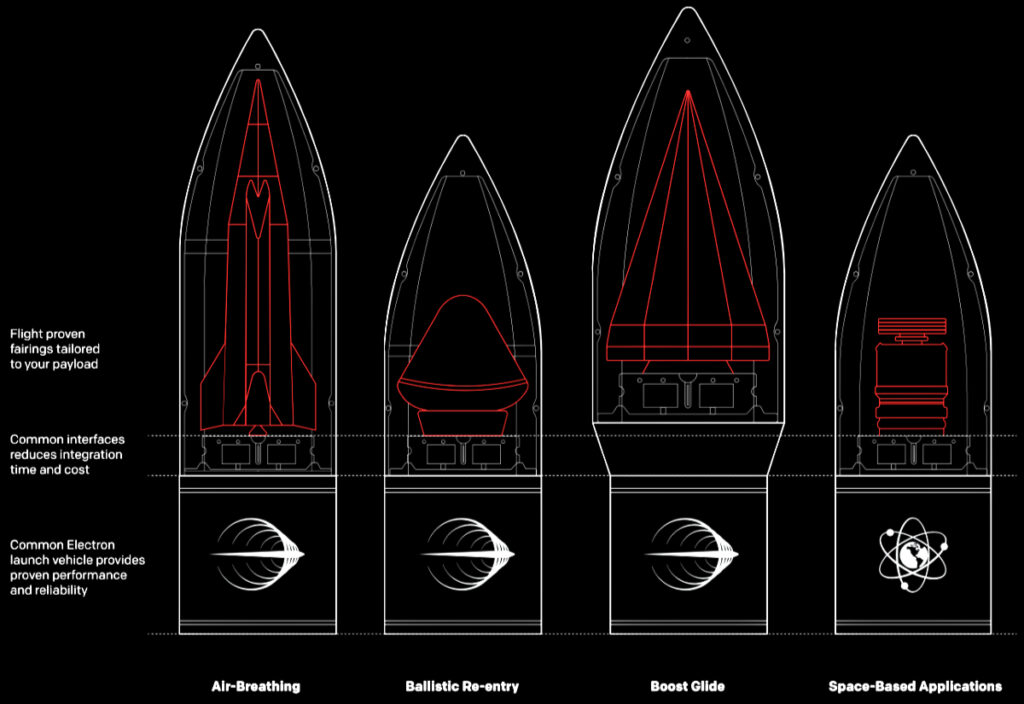
Across both programs, Rocket Lab intends to bid for contracts and task orders served by its Hypersonic Accelerator Suborbital Test Electron (HASTE) launch vehicle, as well as other engineering, design, and launch services. A suborbital variant of Electron—the world’s most frequently launched small orbital rocket—HASTE includes much of the same innovative technology as Electron, including carbon fiber composite structures and 3D printed rocket engines, but has a modified upper Kick Stage tailored for hypersonic technology tests and a larger payload capacity of up to 700 kg / 1,540 lbs.
HASTE can deploy technologies at speeds of more than 7.5km per second to test air-breathing, glide, and ballistic payloads, as well as technologies to re-enter Earth’s atmosphere from space. Successful missions to date include three launches for the U.S. Department of Defense—including twice within just 21 days—from Rocket Lab’s Launch Complex 2 launch site located on Wallops Island, Virginia. Combined, Rocket Lab’s HASTE and Electron launch vehicles have deployed 200+ payloads from its United States and New Zealand launch sites to date.

Rocket Lab founder and CEO, Sir Peter Beck, said, “The ability to contribute toward the collective security of the United States and the United Kingdom across both of these important programs is a proud moment for the HASTE team, and a demonstration of Rocket Lab’s commitment to lead from the front when it comes to innovative and unique solutions for hypersonic technology development. Keeping pace with global developments means more affordable tests at a higher rate that expands the boundaries of hypersonic technology – and that’s a capability we’re already providing all in one platform with HASTE, at a commercial price and cadence that serves the mission of both nations.”