FEATURED
The best of SatNews—essential reads, standout reporting, and hand-picked stories worth your time.
UPDATE 1: SpaceX sends Northrop Grumman’s USSF-67 two satellite mission to orbit via a Falcon Heavy — Northrop Grumman comments
SpaceX has successfully launched the U.S. Space Force's USSF-67 mission from Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A on January 15, 2023, with the liftoff of this National Security Space Launch (NSSL) payload aboard a Falcon Heavy rocket. Both of the ...
The United States + Japan sign a space collaboration agreement
U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken, front left, and Japan’s Minister for Foreign Affairs, Hayashi Yoshimasa, front right, shake hands after signing an agreement Friday, January 13, 2023. During an event hosted by NASA Administrator Bill Nelson and Deputy Administrator ...
UPDATE 4: SpaceX changes date and time of the Starlink launch to January 15th from Vandenberg SFB — while SpaceX Falcon 9 propelled the OneWeb Launch 16 mission to orbit from Canaveral –
SpaceX has moved the date for their Falcon 9 launch of 51 Starlink satellites to LEO from January 14th and is now targeting Sunday, January 15th from Space Launch Complex 4 East (SLC-4E) at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California ...
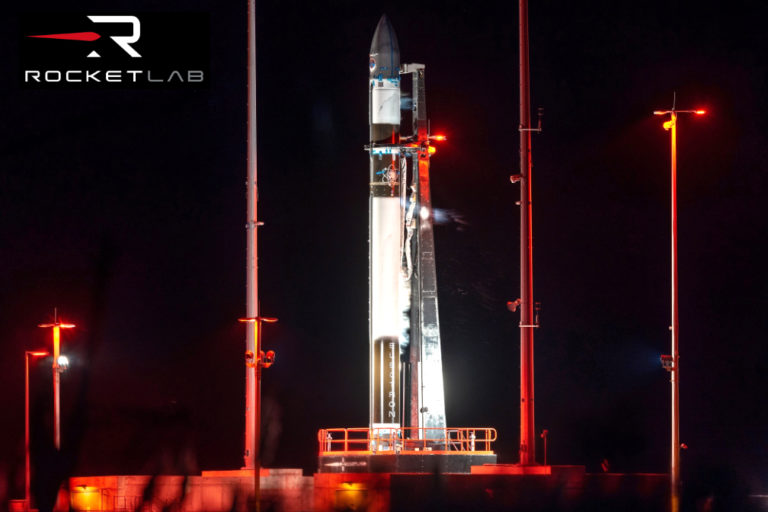
UPDATE 2: Rocket Lab’s 1st U.S. launch for HawkEye 360’s Cluster 6 payload set for January 23rd.
The latest information from Rocket Lab regarding their "Virgina Is For Launch Lovers" mission to occur at NASA's Wallops flight facility is that this event is now scheduled for Monday, January 23rd. There are backup launch dates extending through early ...
Spaceflight signs agreement with Maritime Launch for future Sherpa OTV missions
Spaceflight Inc. has signed an agreement with Maritime Launch Services Inc. (NEO: MAXQ, OTCQB: MAXQF) to launch as many as five Sherpa(™) Orbital Transfer Vehicles (OTVs) — these launches will be from Spaceport Nova Scotia aboard the Cyclone-4M rocket starting ...
Ball Aerospace enters final stages of building USSF’s WSF-M satellite
Artistic rendition of the Weather System Follow-on – Microwave (WSF-M) satellite. Graphic is courtesy of Ball Aerospace. Ball Aerospace has completed the spacecraft bus for the Weather System Follow-on-Microwave (WSF-M) satellite, the U.S. Space Force’s (USSF) next-generation operational environmental satellite ...
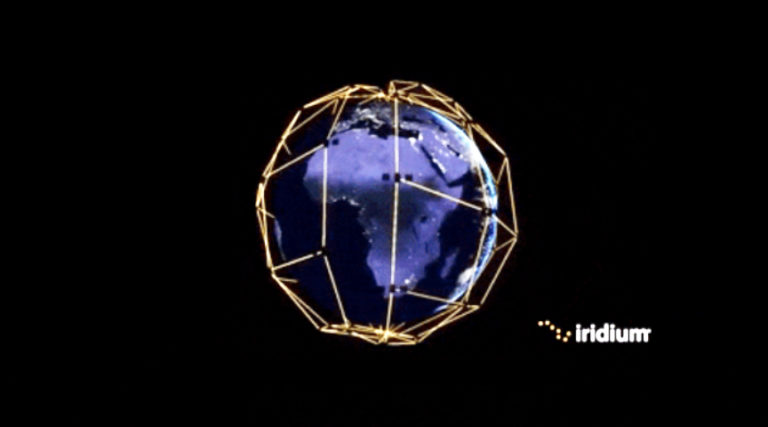
Iridium + Qualcomm to bring satellite messaging to Android smartphones
Iridium Communications Inc. (Nasdaq: IRDM) has entered into an agreement with Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., to enable satellite messaging and emergency services in smartphones powered by Snapdragon® Mobile Platforms. Qualcomm Technologies’ new Snapdragon ® Satellite solution is supported by the fully ...
NOAA’s GOES-18 now GOES West and fully operational with L3Harris’ Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) aboard
Artistic rendition of the GOES WEST (GOES-18) satellite, courtesy of NOAA. NOAA has declared the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES)-18 fully operational as GOES West, marking a significant milestone for severe weather detection in the Western Hemisphere. Launched on March ...
Raytheon Intelligence & Space’s contract with U.S. Space Force for missile track custody system
Raytheon Intelligence & Space has been awarded a prime contract to develop a prototype Missile Track Custody system for the U.S. Space Force. MTC is the service’s first Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) missile tracking system. Under this contract, Raytheon Intelligence & Space ...
Airbus developing two EO satellites for Poland
Airbus Defence and Space has signed a contract with Poland to provide a geospatial intelligence system including the development, manufacture, launch and delivery on-orbit of two, high-performance, optical, EO satellites. This contract also covers the associated ground segment, including Direct ...
SpaceX briskly moves 114 smallsat payloads to orbit with their Transporter-6 mission
The SpaceX launch of their Transporter-6 mission from Cape Canaveral SFS. A Falcon 9 launched the company's Transporter-6 mission from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The first stage booster supporting this mission ...
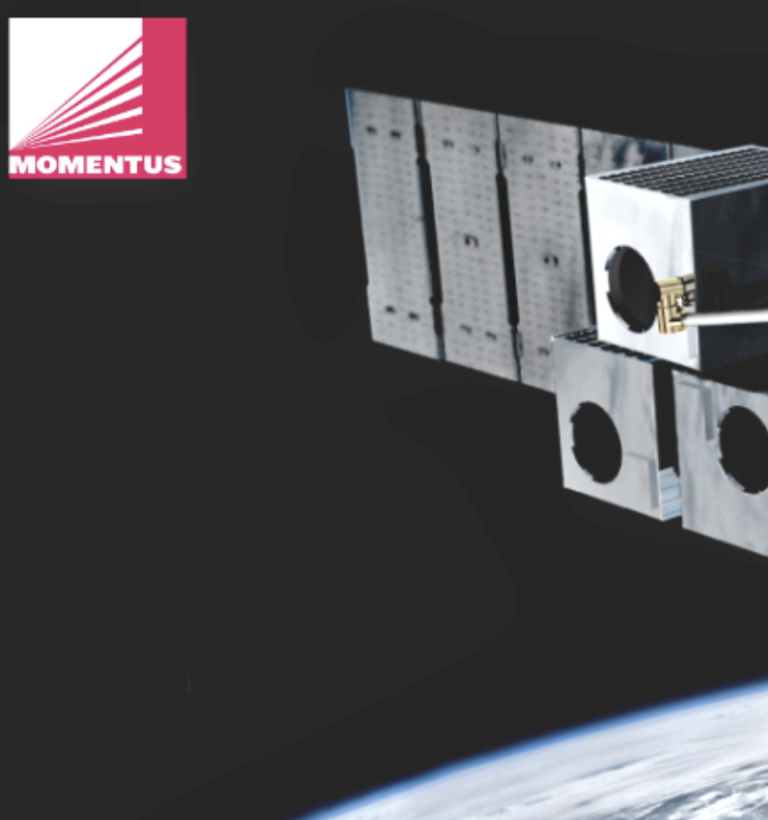
Momentus’ Vigoride OSV heads to orbit via the SpaceX Transporter-6 Falcon 9 launch
Momentus Inc. (NASDAQ: MNTS) launched their 2nd demo flight of the Vigoride Orbital Service Vehicle (OSV) to LEO aboard the SpaceX Transporter-6 mission on January 3rd, 2023. Momentus established contact with the Vigoride vehicle on the spacecraft's first orbital pass ...
Planet Labs launches 36 SuperDove smallsats with SpaceX
Planet Labs PBC launched 36 of their SuperDove satellites, Flock 4y, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on January 3, 2023, at 9:56 a.m., ET (14:56 UTC), on SpaceX’s Transporter-6 mission from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space ...
Launched: SpaceX’s 2Gen Starlink satellites + ImageSat International’s EROS C-3 satellite
SpaceX Starlink satellites en route to their orbits aboard a Falcon 9 launch vehicle. On Wednesday, December 28th at 4:34 a.m., ET, SpaceX launched 54 Starlink satellites to LEO from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Space Force ...
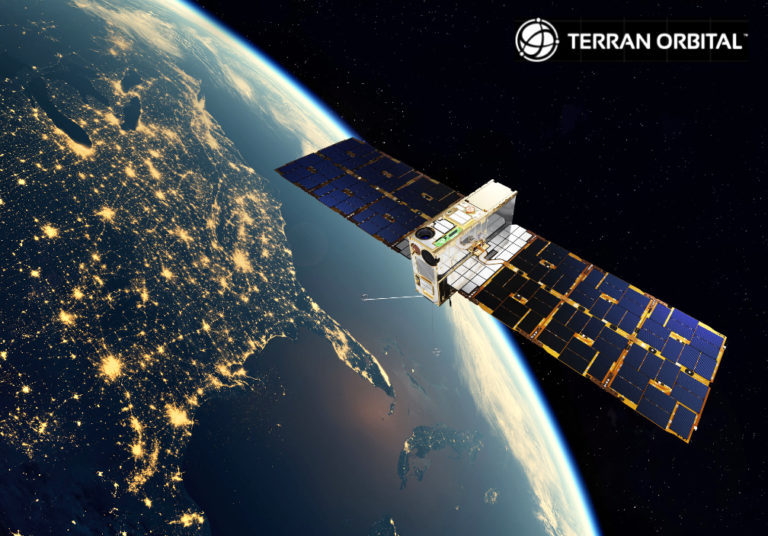
Terran Orbital delivers 10 satellite buses to prime Lockheed Martin for SDA Tranche 0 integration
Terran Orbital Corporation (NYSE: LLAP) has delivered the final ten satellite buses to prime contractor Lockheed Martin in support of the Space Development Agency’s (SDA) Tranche 0 Transport Layer. The delivery of the ten Tranche 0 buses demonstrates Terran Orbital’s ...
Europe’s first satellite launch complex to be inaugurated in Northern Sweden
On January 13, 2023, the Swedish head of state, King Carl XVI Gustaf, together with European and Swedish political dignitaries, will visit Esrange Space Center in northern Sweden to cut the ribbon of a new spaceport that will significantly reshape ...
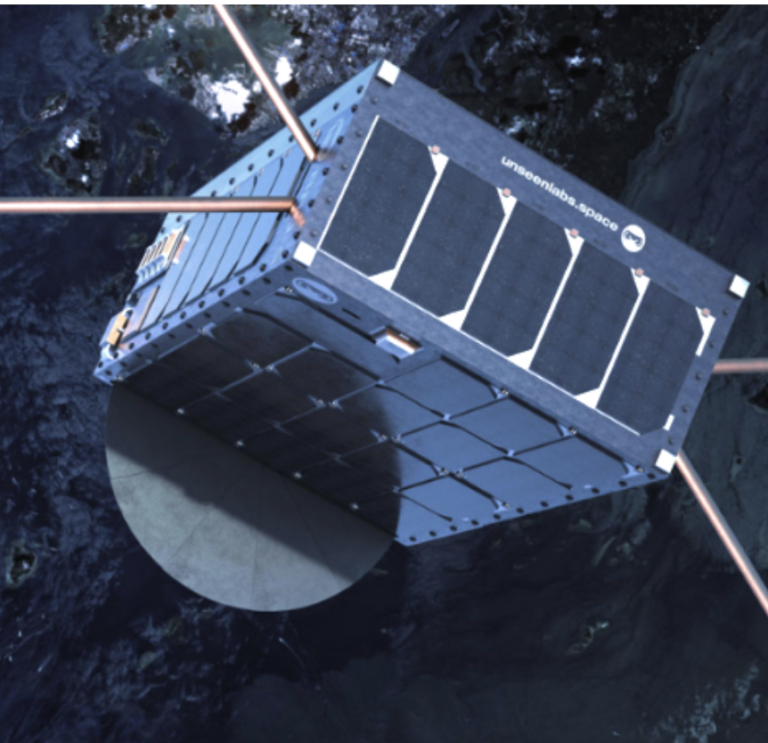
Exolaunch to deploy Unseenlabs’ BRO-8 smallsat into orbit
Unseenlabs has signed a launch services agreement (LSA) with Exolaunch to deploy their BRO-8 smallsat on SpaceX’s Transporter-6 rideshare mission, which is to launch no earlier than (NET) January of 2023. Manufactured by GOMSpace, BRO-8 (Breizh Reconnaissance Orbiter-8) is a ...
Momentus engages in a 2nd launch management agreement with Australia’s CUAVA
Momentus Inc. (NASDAQ: MNTS) has an agreement with the Australian Research Council Training Centre for CubeSats, Uncrewed Aerial Vehicles, and their Applications (CUAVA), for the transportation of the Waratah Seed WS-1 CubeSat to LEO in October of 2023. The Waratah ...
UK Space regulator issues Virgin Orbit launch licenses
The UK Civil Aviation Authority has issued the final, remaining licenses to Virgin Orbit ahead of the company's planned UK launch after the agency's requirements were met within 15 months. The licenses were issued following consent from Transport Secretary Mark ...
UPDATE 4: Arianespace + ESA appoint an independent inquiry mission to investigate the Flight VB22 launch failure
The Arianespace Vega C VV22 launch vehicle lifted off as scheduled on December 20, 2022 at 10:47 p.m. (local time in French Guiana). The lift-off, the mission and the separation of the first stage (P120C) were nominal. Following the nominal ...