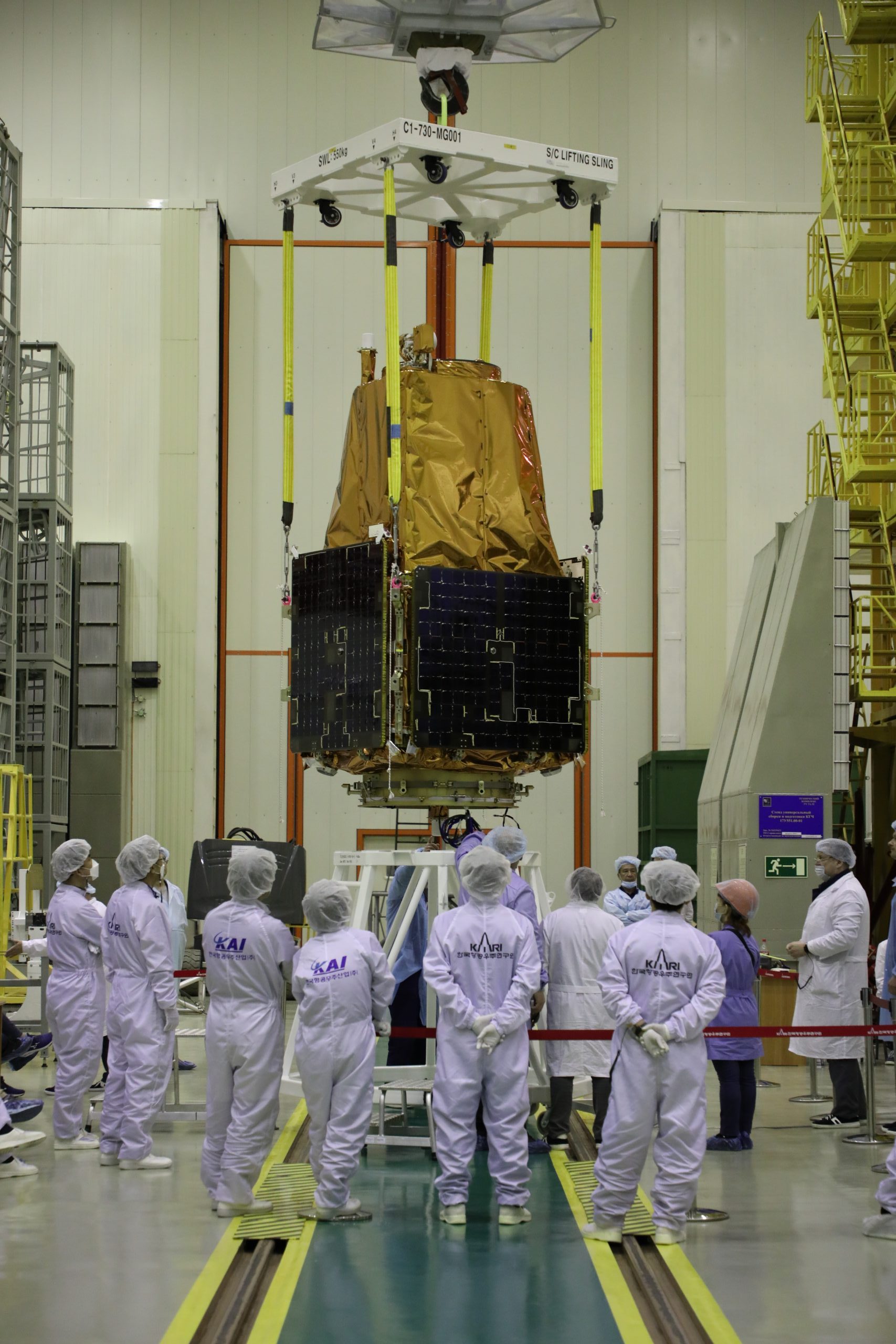
Eutelsat Communications (Euronext Paris: ETL) has signed a contract with Airbus for the procurement of EUTELSAT 36D to succeed EUTELSAT 36B, expected to reach its end of life at the end of 2026, at the key 36° East orbital position.

With coverage of Africa, Russia and Europe, 36° East is a key orbital slot for Eutelsat, ranking third in terms of overall revenue generation, after 13° East (HOTBIRD) and 7/8° West, and second for Government Services, with an exceptional fill rate reflecting the ongoing robust demand in its footprint. Eutelsat’s two satellites, EUTELSAT 36B and EUTELSAT 36C, together notably support the broadcast businesses of major anchor customers including Multichoice and ZAP in Africa and Tricolor and NTV+ in Russia.

With 70 physical Ku-band transponders, the all-electric EUTELSAT 36D will assure all the main legacy missions of EUTELSAT 36B, with enhancements to coverage areas and performance. Based on the state-of-the-art Airbus Eurostar Neo platform, it combines increased payload capacity and more efficient power and thermal control systems with reduced production time and optimised costs.
The satellite is due for launch in the first half of 2024 with a substantial protection loop that reflects its mission-critical importance to its main customers. This procurement does not alter Eutelsat’s capital expenditure objective.
Pascal Homsy, Eutelsat’s Chief Technical Officer, said: “We are delighted to rely once again on one of our longstanding partners, Airbus, to assure this critical satellite program. This new state-of-the-art satellite will assure enhanced service continuity for our key DTH customers in the major markets of Africa and Russia.”
François Gaullier, head of Telecom Systems at Airbus, added, “We are delighted to help Eutelsat provide broadcast and data connectivity, including to remote regions where it’s needed most. More personally, the continuing confidence of Eutelsat in our products is high praise of the reliability of our work and a source of pride for our skilled teams.”