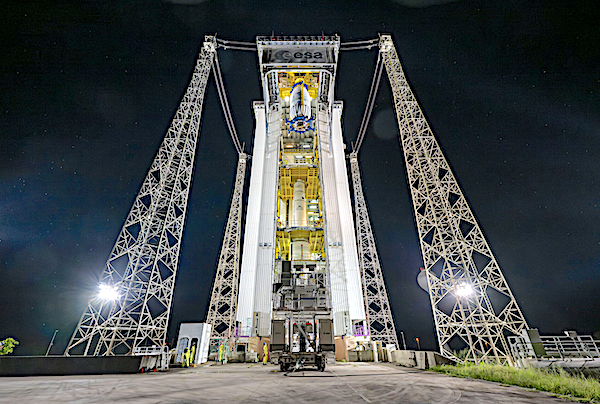


Vega-C is scheduled to launch from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana at 23:03 local time on July 25, (03:03 BST/04:03 CEST on 26 July), Friday, July 25th, 7:03 PM PDT. Flight VV27 will be operated by Arianespace and launch Airbus’s four CO3D satellites and the French space agency CNES MicroCarb mission.

Tune in on July 26, from 03:40 CEST to watch the Vega-C rocket take flight once again. The livestream is available in English, French and Italian.
The four small satellites in the CO3D constellation (an abbreviation of the French ‘Constellation Optique en 3D’) are set to map the globe in three dimensions from low Earth orbit, to serve public and private sector needs.
MicroCarb is designed to map sources and sinks of carbon dioxide on a global scale. ESA coordinated and procured the launch of MicroCarb on behalf of the European Commission, as part of its In-Orbit Demonstration / In-Orbit Validation (IOD/IOV) program.
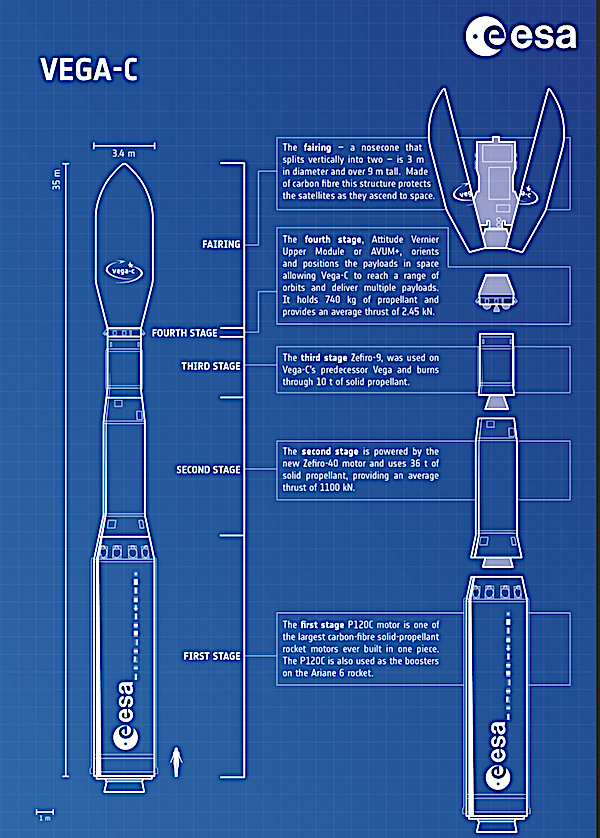
Europe’s Vega-C rocket can launch 2300 kg into space, such as small scientific and Earth observation spacecraft. At 35 m tall, Vega-C weighs 210 tonnes on the launch pad and reaches orbit with three solid-propellant-powered stages before the fourth liquid-propellant stage takes over for precise placement of satellites into their desired orbit around Earth. Vega-C is the evolution of the Vega family of rockets and delivers increased performance, greater payload volume and improved competitiveness.
Complementing the Ariane family to launch all types of payloads into their desired orbits, Vega-C ensures that Europe has versatile and independent access to space. ESA leads the Vega-C programme, working with Avio as prime contractor and design authority. Arianespace is the launch service provider for this launch.
Arianespace to launch Airbus Defence and Space’s CO3D satellites and CNES’s MicroCarb satellite on July 25 from French Guiana

On Friday July 25th, 2025, at 11:03 p.m. local time (02:03 a.m. UTC, 04:03 a.m. CEST, on July 26th, 2025), Arianespace is to launch Airbus Defence and Space’s CO3D satellites, as well as the CNES’s MicroCarb satellite. This mission, called “VV27” will be performed using an Arianespace operated Vega C rocket, launched from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana.

The main passengers, the four satellites composing the CO3D constellation, as well as the auxiliary passenger, MicroCarb, will be placed in Sun-synchronous orbits. The expected total duration of the mission (from lift-off to separation of all satellites) is 1 hour and 41 minutes.
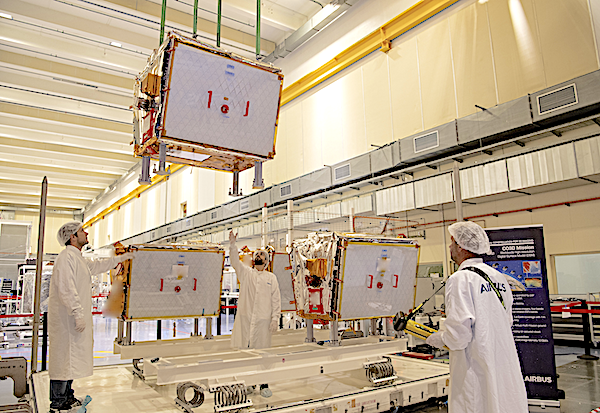

Designed and built by Airbus, the CO3D (Constellation Optique 3D) satellites will deliver a global high-resolution Digital Surface Model (DSM) service to CNES providing 50 cm stereo imagery as well as 2D imagery for government and commercial customers. A partnership between Airbus and CNES, CO3D comprises four dual-use satellites, each based on all-electric platforms and weighing around 285kg. This data will feed a cloud-based ground segment operated by Airbus, including an image processing chain delivered by CNES. This data will answer both the military need for precise and up-to-date cartography as well as civil applications such as hydrology, geology, civil security, urban planning and land and resource management.
The CNES’ MicroCarb mission is designed to map sources and sinks of carbon dioxide (CO₂), the most important greenhouse gas, on a global scale. The satellite’s dispersive spectrometer instrument will measure atmospheric concentration of CO₂ globally with a high degree of precision. MicroCarb’s platform is based out of the lastest CNES Myriade model. Its instrument was built by Airbus Defence and Space, and the integration was realized by Thales Alenia Space UK through a dedicated partnership implemented with the UK Space Agency.
The VV27 launch at a glance:
108thspacecraft built by Thales Alenia Space launched by Arianespace (MicroCarb platform)
354th launch by Arianespace, 5th Vega C launch
10% of the satellites launched by Arianespace are Earth observation satellites
147th-150th spacecraft built by Airbus Defence and Space launched by Arianespace (CO3D, 4 satellites)
Arianespace to launch CO3D + MicroCarb satellites via Vega C
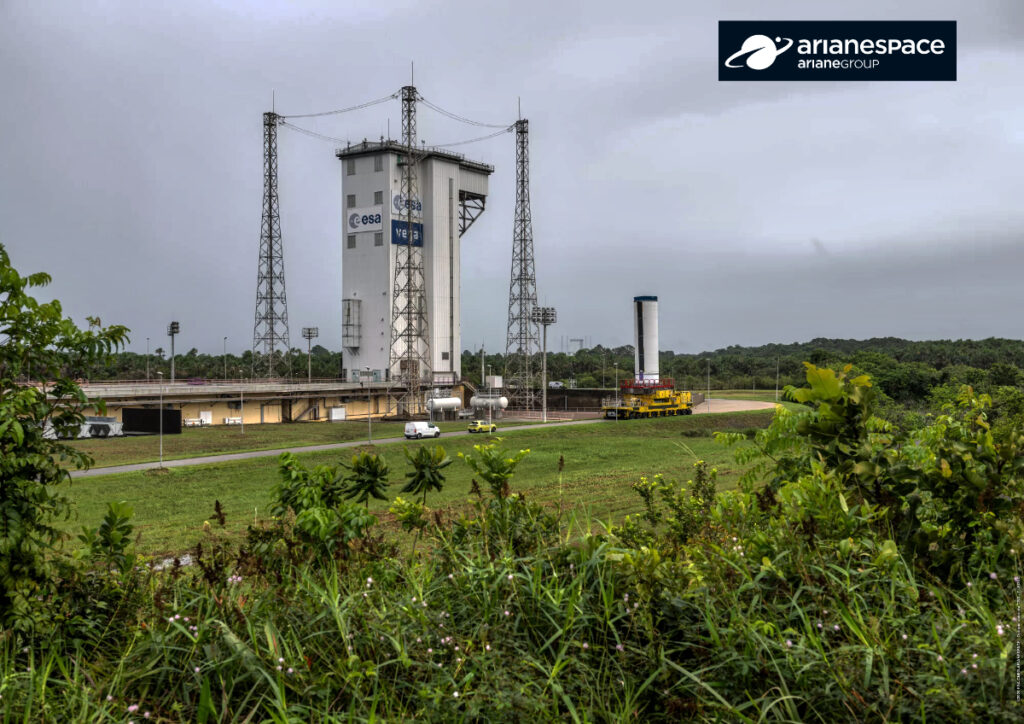

On July 25, 2025, Arianespace will place into orbit Airbus Defence and Space’s CO3D satellites, as well as the CNES’s MicroCarb satellite, with a Vega C rocket.
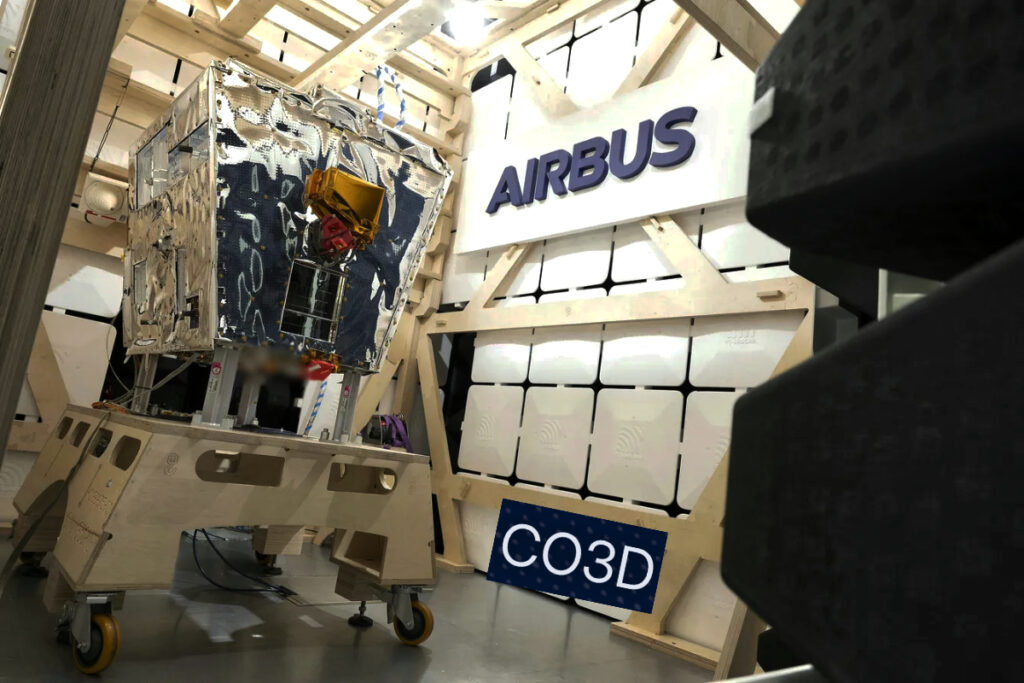

The CO3D mission is a constellation (Constellation Optique en 3D) composed of four small satellites which are set to map the globe in 3D from LEO, serving public and private sector needs.
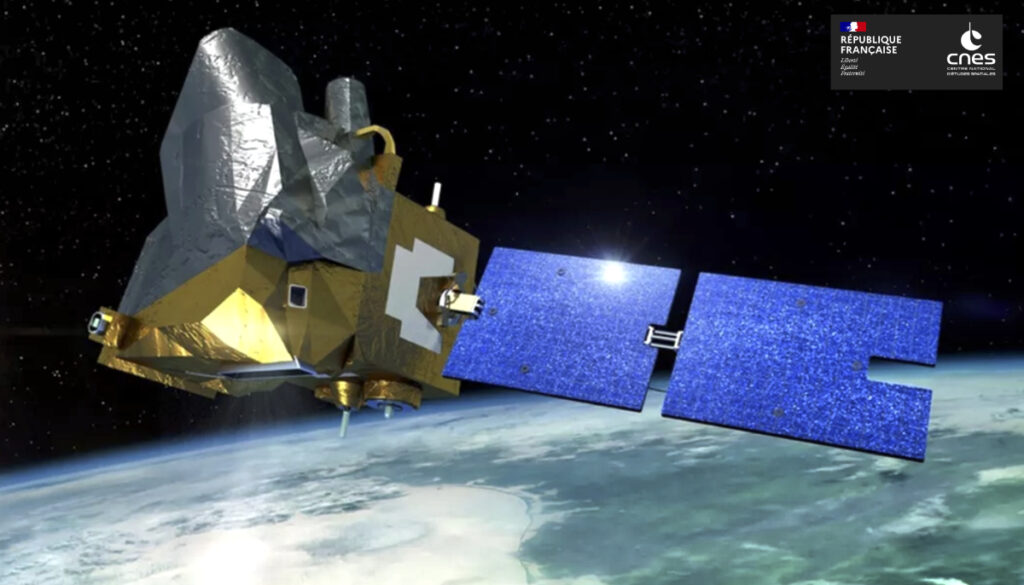

The MicroCarb mission is designed to map sources and sinks of carbon dioxide (CO2) – the most important greenhouse gas – on a global scale.
This data will answer both the military need for precise and up-to-date cartography as well as civil applications such as hydrology, geology, civil security, urban planning and land and resource management.
The CNES’ MicroCarb mission is designed to map sources and sinks of carbon dioxide (CO₂), the most important greenhouse gas, on a global scale. The satellite’s dispersive spectrometer instrument will measure atmospheric concentration of CO₂ globally with a high degree of precision.
MicroCarb’s platform is based out of the lastest CNES Myriade model. Its instrument was built by Airbus Defence and Space, and the integration was realized by Thales Alenia Space UK through a dedicated partnership implemented with the UK Space Agency.
The VV27 launch at a glance:
- 354th launch by Arianespace, 5th Vega C launch
- 10% of the satellites launched by Arianespace are Earth observation satellites
- 147th-150th spacecraft built by Airbus Defence and Space launched by Arianespace (CO3D, 4 satellites)
- 108th spacecraft built by Thales Alenia Space launched by Arianespace (MicroCarb platform)
