
Starfish Space has been awarded SBIR Phase III funding for a mission to inspect defunct satellites to increase opportunities to mitigate space debris.
NASA is advancing an innovative approach to enabling commercial inspection of defunct, or inoperable, satellites in low Earth orbit, a precursor to capturing and repairing or removing the satellites.
The agency has awarded Starfish Space a Phase III Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) contract to complete the Small Spacecraft Propulsion and Inspection Capability (SSPICY) mission. The award follows a Phase III study, which funded four, U.S. small businesses, including Starfish, to develop mission concepts. Starfish Space will receive $15 million over three years to execute the mission.
The ability to inspect defunct spacecraft and identify opportunities for repair or deorbiting is critical to maintaining a safe orbital environment for spacecraft and humans. Orbital debris mitigation is a key component of NASA’s Space Sustainability Strategy.

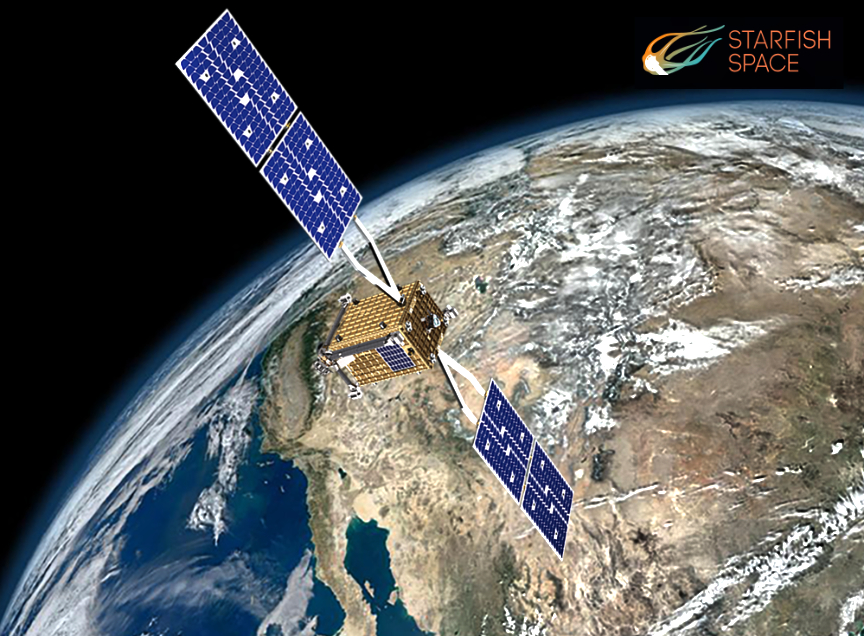
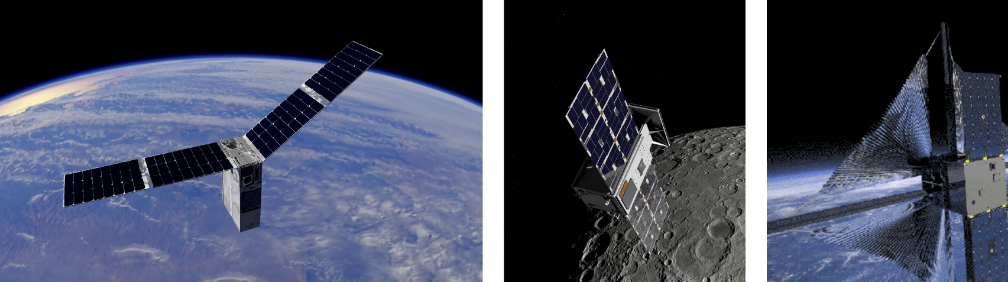
The Starfish-led mission uses the company’s Otter spacecraft, a small satellite about the size of an oven, which is designed to inspect, dock with, and service or deorbit other satellites. Otter’s electric propulsion system will not only help it efficiently travel to multiple satellites, but the SSPICY demonstration also will mature the spacecraft’s ability to perform inspections using electric propulsion, an important enabling technology not typically used for rendezvous and proximity operations.
During the SSPICY mission, Otter will visit and inspect multiple U.S. owned defunct satellites that have agreed to be visited and inspected – a delicate and challenging task, as satellites move quickly and are kept far apart from each other for safety. Otter will approach within hundreds of meters of each satellite to conduct inspections during mission operations. During the inspection, Otter will gather key information about each of the debris objects including their spin rate, spin axes, and current conditions of the objects’ surface materials.
The SSPICY mission is the first commercial space debris inspection funded by NASA and supports the agency’s efforts to extend the life of satellites while reducing space debris. Satellites that are no longer in use can break apart or collide with one another, creating debris clouds that pose risk to human spaceflight, science and robotic missions in Earth’s orbit, and missions to other planets in the solar system. Data from inspections like those planned during the SSPICY demonstration will play a critical role in understanding the nature of defunct satellites and advancing solutions for reuse or disposal.
“The SSPICY mission is designed to mature technologies needed for U.S. commercial capabilities for satellite servicing and logistics or disposal,” said Bo Naasz, senior technical lead for in-space servicing, manufacturing, and assembly in NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate. “In-space inspection helps us characterize the physical state of a satellite, gather data on what may leave spacecraft stranded, and improve our understanding of fragmentations and collisions, a difficult but critical factor in a sustainable space operating environment.”
“We are excited to expand our partnership with NASA, building on our shared commitment to advancing in-space manufacturing and assembly capabilities,” said Trevor Bennett, co-founder of Starfish Space. “It’s an honor for Starfish to lead the first commercial debris inspection mission funded by NASA. We look forward to collaborating on this and future satellite servicing missions to enable a new paradigm for humanity in space.”
The Otter spacecraft is expected to launch in late 2026 and will begin performing inspections in 2027.
The SSPICY demonstration is funded and managed by NASA’s Small Spacecraft Technology program based at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley. The award is enabled by NASA’s SBIR program, which is open to U.S. small businesses to develop an innovation or technology. These programs are part of NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate.

Article author: Tara Friesen
Learn more at:
