
Interstellar Technologies Inc. successfully passed the stage-gate review for the Small Business Innovation Research Program Phase 3 (SBIR Phase 3) on September 19, 2024. Administered by the Government of Japan’s Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) to promote R&D in startups, the program will grant Interstellar up to 4.63 billion Yen in new funding.
The Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program aims to promote the practical application of advanced technologies developed by startups and similar entities. Under this initiative, companies in the space sector focused on the development and testing of private rockets can receive up to ¥14 billion by Phase 3, with the program running through fiscal year 2027. Interstellar was selected for Phase 1 of this project in September 2023, with a grant of up to ¥2 billion. After successfully passing the stage-gate review, the company has now advanced to Phase 2, securing a grant of up to ¥4.63 billion.
Global demand for small satellite launches has surged since the 2010s, driven by the rise of private space enterprises, growing importance in the security sector, and the emergence of new applications like satellite constellations. The number of satellites weighing 1,200 kg or less launched increased from 2,429 in 2022 to 2,860 in 2023, marking a 20-fold rise since 2016. Despite this growth, the supply of space transportation services continues to lag behind demand, creating a significant bottleneck in the industry. In Japan, launch opportunities remain scarce, with only a few conducted annually, leading many Japanese satellite operators to rely on overseas providers.
In response to these challenges, the Japanese government has set a target of achieving 30 domestic rocket launches annually by the early 2030s. This goal, part of the Space Strategy Fund Basic Policy, involves utilizing both government and commercial rockets to address various launch needs both domestically and internationally. Interstellar is committed to advancing Japan’s independent access to space through the development of ZERO, a low-cost, high-frequency rocket designed for launching small satellites. The company also aims to establish a globally competitive space transportation system.

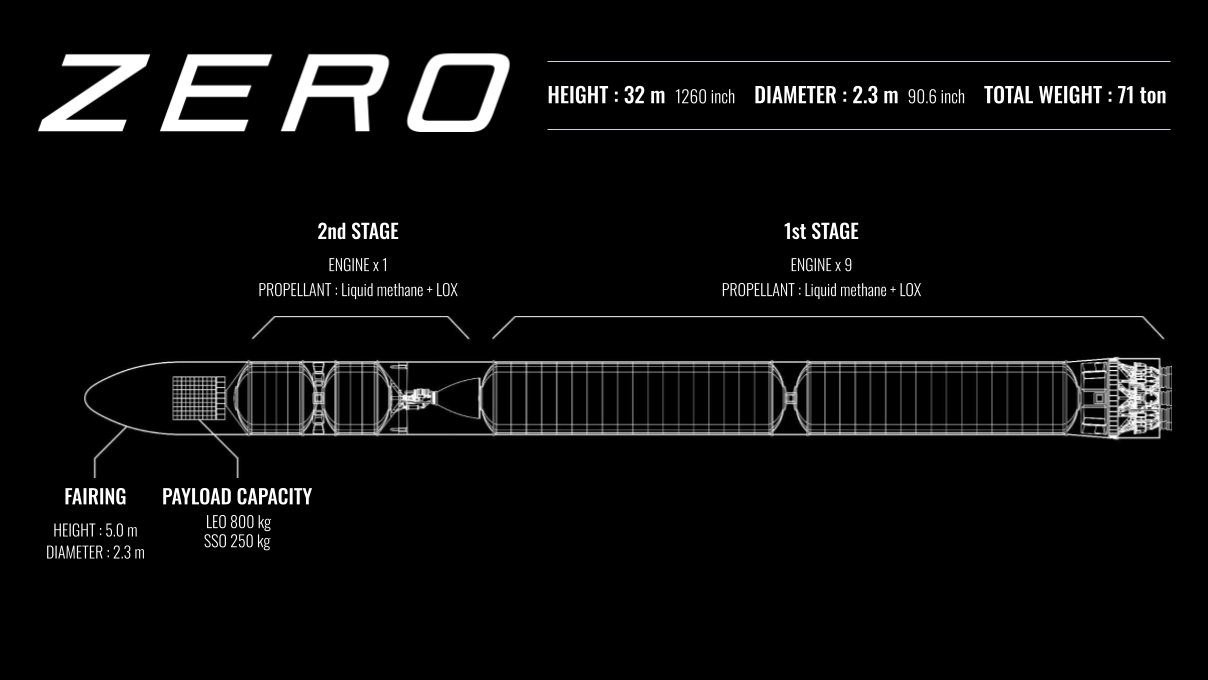
ZERO Specifications
Height: 32 m
Diameter: 2.3 m
Launch Mass: 71 ton
Fuel: Liquid Bio-methane Oxidizer: Liquid Oxygen
Number of Engines: 1st Stage x 9, 2nd Stage x 1
Payload Capacity: LEO 800 kg / SSO 250 kg
ZERO is an orbital class launch vehicle designed to meet the growing demand for small satellite launches. Building on the expertise gained from the successful launch of MOMO, Japan’s first private suborbital launch vehicle, Interstellar is advancing toward the inaugural launch of ZERO.
In response to growing global and regional demand, ZERO is increasing its capacity to launch satellites of up to 800 kilograms into LEO. This strategic enhancement strengthens Japan’s independent space transportation capabilities and positions Interstellar to establish a strong foothold in both the Asia-Oceania and European markets.
Takahiro Inagawa, Chief Executive Officer of Interstellar Technologies Inc., said, “We are honored to have our achievements over the past year in the SBIR Phase 3 project recognized and selected for the next phase following a rigorous evaluation process. We feel the growing demand for rockets, which are essential for autonomy and the expansion of the space market within Japan, on a daily basis. Building on the extensive accomplishments we have achieved since our founding, we will continue our unwavering efforts to become a comprehensive infrastructure company in the space industry.”
ZERO’s space transportation service stands out with competitive pricing—under ¥800 million per launch (in mass production)—enabled by an integrated development and manufacturing process. Additionally, ZERO offers the flexibility of customized launches, tailored to the specific needs of satellite companies. For satellite operators in Japan, Asia, and Oceania, proximity to the launch site provides added convenience, reducing both launch-related time and costs, ultimately enhancing overall value.
