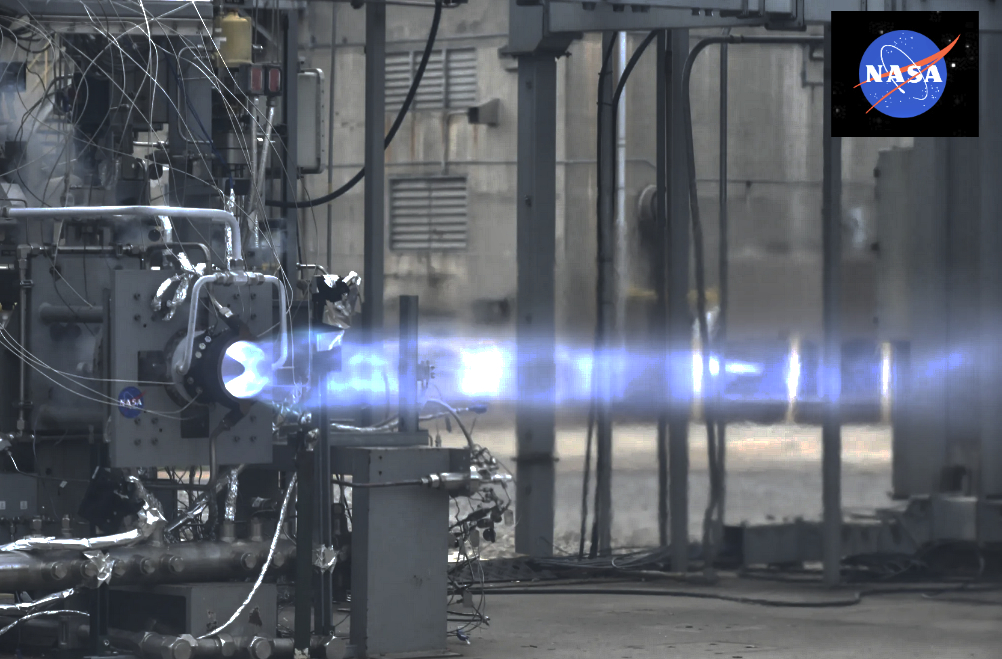
NASA has achieved a new benchmark in developing an innovative propulsion system called the Rotating Detonation Rocket Engine (RDRE). Engineers at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, successfully tested a novel, 3D-printed. RDRE for 251 seconds (or longer than four minutes), producing more than 5,800 pounds of thrust.
That kind of sustained burn emulates typical requirements for a lander touchdown or a deep-space burn that could set a spacecraft on course from the Moon to Mars, said Marshall combustion devices engineer Thomas Teasley, who leads the RDRE test effort at the center.
“The RDRE enables a huge leap in design efficiency,” Teasley said. “It demonstrates we are closer to making lightweight propulsion systems that will allow us to send more mass and payload further into deep space, a critical component to NASA’s Moon to Mars vision.”
RDRE’s first hot fire test was performed at Marshall in the summer of 2022 in partnership with In Space LLC and Purdue University, both of Lafayette, Indiana. That test produced more than 4,000 pounds of thrust for nearly a minute. The primary goal of the latest test, Teasley noted, is to better understand how to scale the combustor to different thrust classes, supporting engine systems of all types and maximizing the variety of missions it could serve, from landers to upper stage engines to supersonic retropropulsion, a deceleration technique that could land larger payloads – or even humans – on the surface of Mars.
Select this link for a full video
Engineers at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland and researchers at Venus Aerospace of Houston, Texas, are working with NASA Marshall to identify how to scale the technology for higher performance.
RDRE is managed and funded by the Game Changing Development Program within NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate.
