With less than 100 days to go before the October 5 launch, NASA’s Psyche spacecraft is undergoing final preparations at Cape Canaveral, Florida — teams of engineers and technicians are working almost around the clock to ensure the orbiter is ready to journey 2.5 billion miles (4 billion kilometers) to a metal-rich asteroid that may tell us more about planetary cores and how planets form.
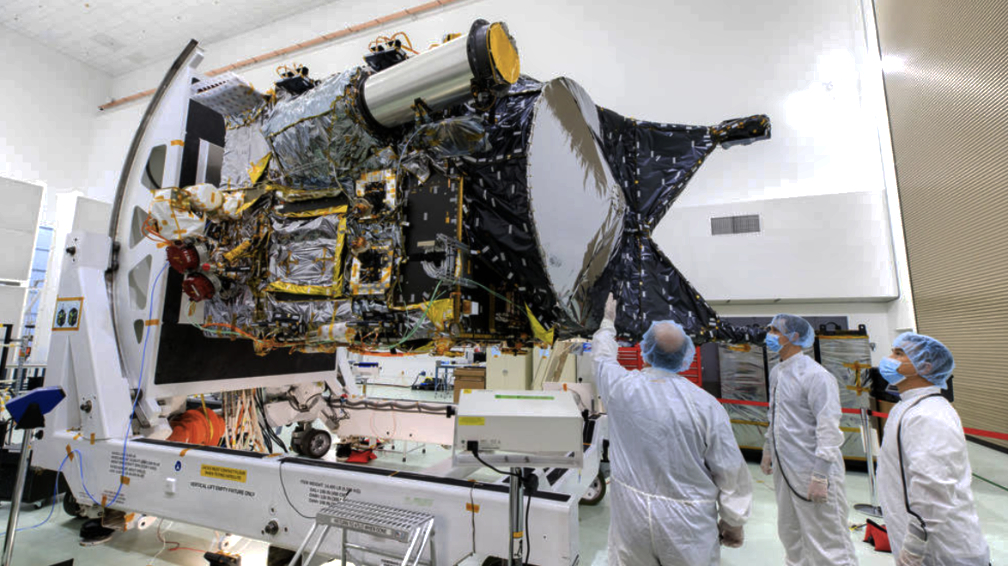

Photo is courtesy of NASA/Frank Michaux
The mission team recently completed a comprehensive test campaign of the flight software and installed it on the spacecraft, clearing the hurdle that kept Psyche from making its original 2022 launch date.
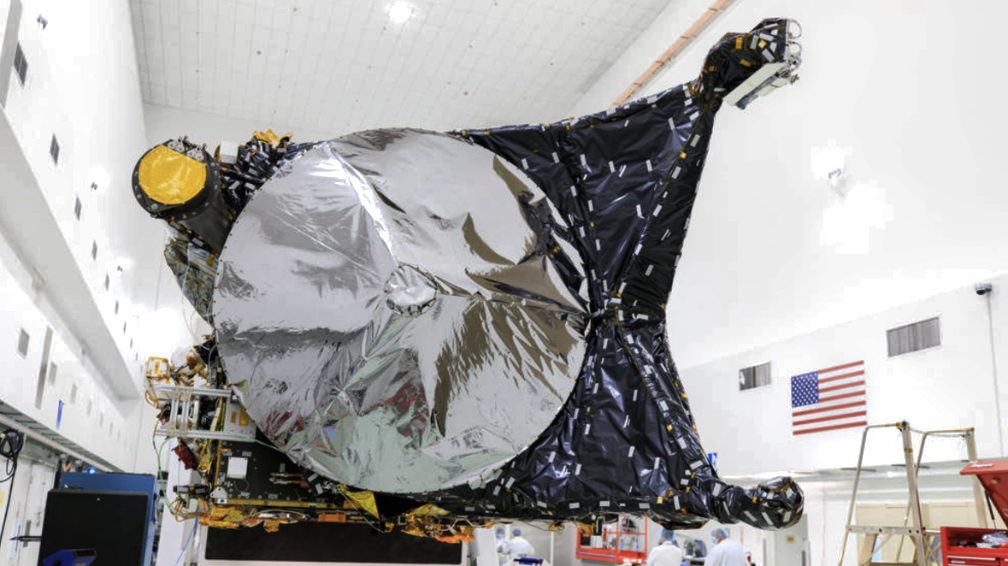

Photo is courtesy of NASA/Frank Michaux.
Psyche is set to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy (the first interplanetary launch for that rocket) from Space Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center at 10:38 a.m. EDT (7:38 a.m. PDT) on October 5, with additional opportunities scheduled through October 25. After escaping Earth’s gravity, the Psyche spacecraft will use solar electric propulsion to accomplish its six-year journey to asteroid Psyche.
Measuring about 173 miles (279 kilometers) at its widest point, the asteroid Psyche presents a unique opportunity to explore a metal-rich body that may be part of a core of a planetesimal, the building block of an early planet. Once the spacecraft reaches Psyche in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, it will spend at least 26 months orbiting the asteroid, gathering images and other data that will tell scientists more about its history and what it is made of.
However, first, a team of 30 or so engineers and technicians will wrap up the assembly, test, and launch operations phase of the mission. The team recently finished several weeks of functional testing of the science instruments as well as the spacecraft hardware and software.
After removing the last of the cables that snake around the hardware for testing, they’ll “close out” the spacecraft by reinstalling some exterior panels that had been removed for access and complete the thermal blanketing. Later in July, they will integrate and test the deployment of the enormous solar arrays. Then, in mid-August, a crew will begin slowly loading all 2,392 pounds (1,085 kilograms) of propellant – the neutral gas xenon – onto the spacecraft over the course of a couple weeks.
“The team and I are now counting down the days to launch. Our focus has shifted to safely completing the final mechanical closeout of the spacecraft and preparing the team for operations. The team is conducting numerous training activities to ensure that we are prepared and ready. It’s a very busy time, but everyone is very excited and looking forward to the launch.” — Henry Stone, Psyche’s project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory
“We are moving forward, and we’re confident that when we’re on the pad, we’ll be ready to hit the button. For all of us, we’ll be excited to launch this bird.” — Luis Dominguez, systems and electrical lead for assembly, test, and launch operations, Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Arizona State University leads the Psyche mission. A division of Caltech in Pasadena, JPL is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and test, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power, solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis.

JPL also is providing a technology demonstration instrument called Deep Space Optical Communications that will fly on Psyche in order to test high-data-rate laser communications that could be used by future NASA missions.

Psyche is the 14th mission selected as part of NASA’s Discovery Program, managed by the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.