Northrop Grumman Corporation (NYSE: NOC) has conducted a successful flight test of the company’s advanced airborne navigation solution, Embedded Global Positioning System (GPS) / Inertial Navigation System (INS) Modernization, known as EGI-M. This is the first time that EGI-M, equipped with an M-Code capable receiver, has been tested in flight.
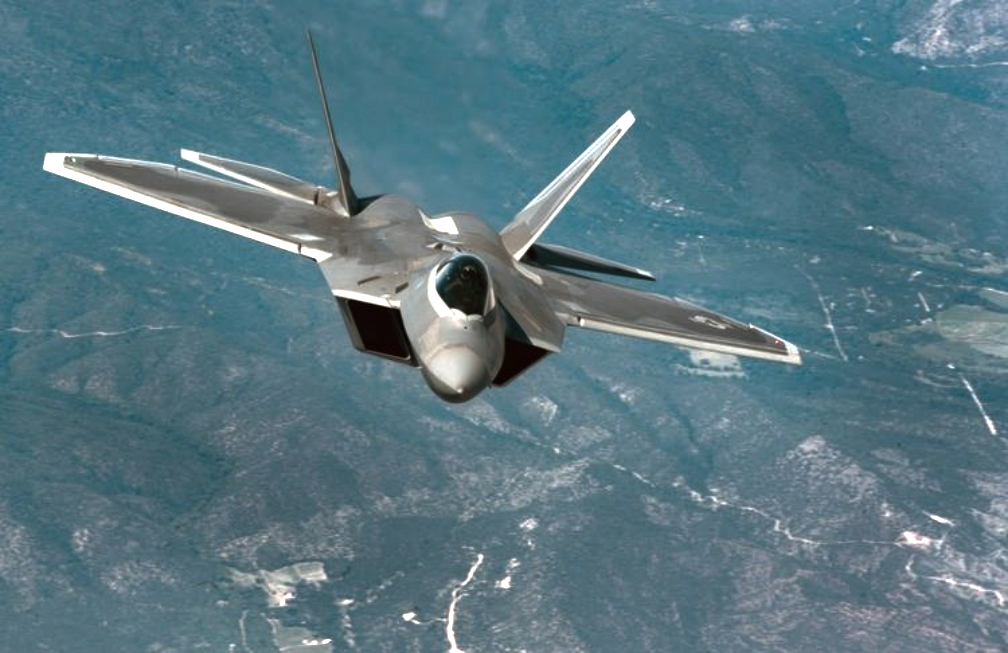

U.S. Air Force Photo/Staff Sgt. Carlin Leslie.
M-Code technology enables missions to be conducted in GPS-contested and GPS-denied environments.
The M-Code capable GPS receiver is a core component of Northrop Grumman’s EGI-M program, engineered to quickly transmit positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) information.
The fully operational EGI-M system will feature a modular platform interface, designed to easily integrate with current platform navigation systems, supporting advanced software and hardware technology upgrades now and in the future.
Testing occurred in May aboard a testbed aircraft. Flight test data confirmed that Northrop Grumman’s prototype EGI-M solution, the M-Code capable LN-351, performed at standards equal to the current LN-251 INS / GPS system, featuring modern fiber optic gyro technology.

Critical design review for EGI-M was completed in 2020. Launch platforms for Northrop Grumman’s EGI-M are the E-2D Advanced Hawkeye and the F-22 Raptor. Additional fixed-wing and rotary-wing platforms across Department of Defense and allied forces have selected Northrop Grumman’s EGI-M as their future navigation solution to support mission-critical systems.

“This flight test is a major step forward in developing our next generation airborne navigation system. The EGI-M capability developed by Northrop Grumman enables our warfighters to navigate accurately and precisely through hostile and contested environments.” — Ryan Arrington, Vice President, navigation and cockpit systems, Northrop Grumman