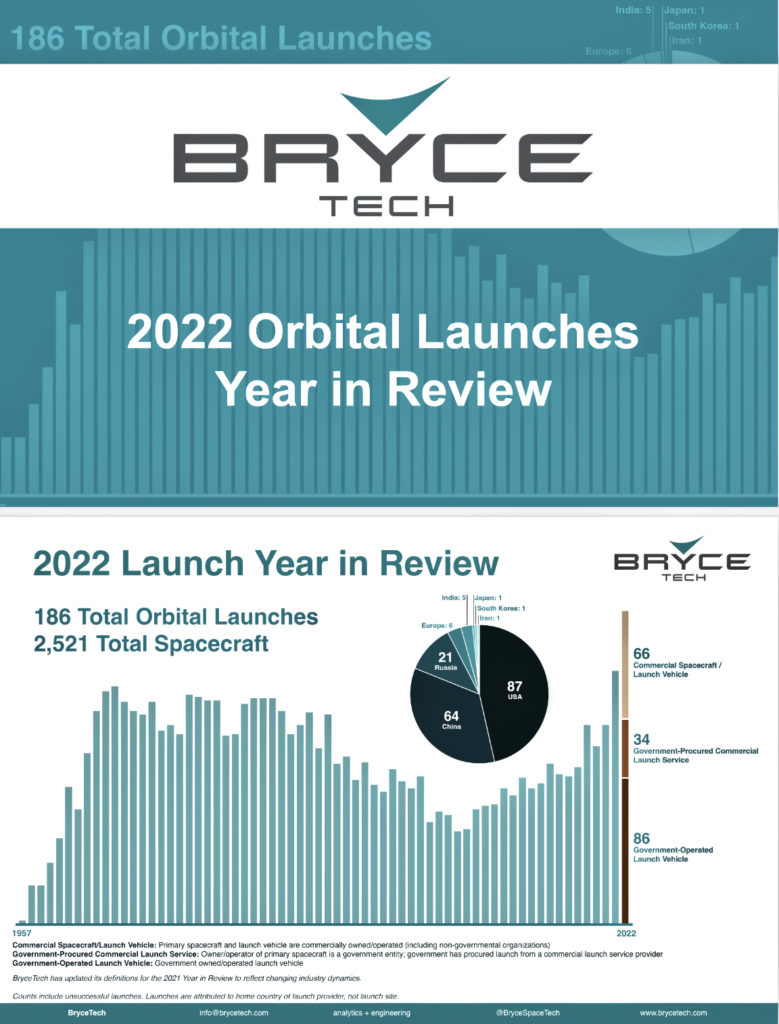
Highlights:
- A record-breaking 186 orbital launches by service providers worldwide.
- 2,521 spacecraft launched—the highest number since Sputnik was sent into orbit in 1957.
- Six launches ended in failure, with 32 spacecraft never making it to orbit.
- Approximately 1,000,000 kilograms of total mass launched — the largest amount destined for orbit in a single calendar year.
- U.S. launch service providers conducted the majority of launches — a total of 87 (85 of these were successful).
- With a total of 61 launches, SpaceX conducted the most launches in 2022 — all of which were successful (an average cadence of one launch every six days).
- About 50% of SpaceX launches supported deployment of the company’s Starlink constellation, reaching 3,300 operational satellites in orbit at the end of 2022.
- Chinese providers conducted 64 launches, most managed by China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), which launched one per week on average.
- Most launches (46%) were conducted by government entities that build, own, and operate vehicles. The majority of these were accomplished by China’s CASC.
- About 35% of the launches were of commercial spacecraft carried by commercial vehicles, with missions as varied as cargo delivery to the International Space Station (ISS) to routine deployment of telecommunications satellites to geosynchronous orbit (GEO).
- 18% of launches were conducted by companies serving government clients; spacecraft owned and operated by the U.S. government and launched aboard vehicles owned by SpaceX, Rocket Lab, and United Launch Alliance (ULA) are representative of this category.
