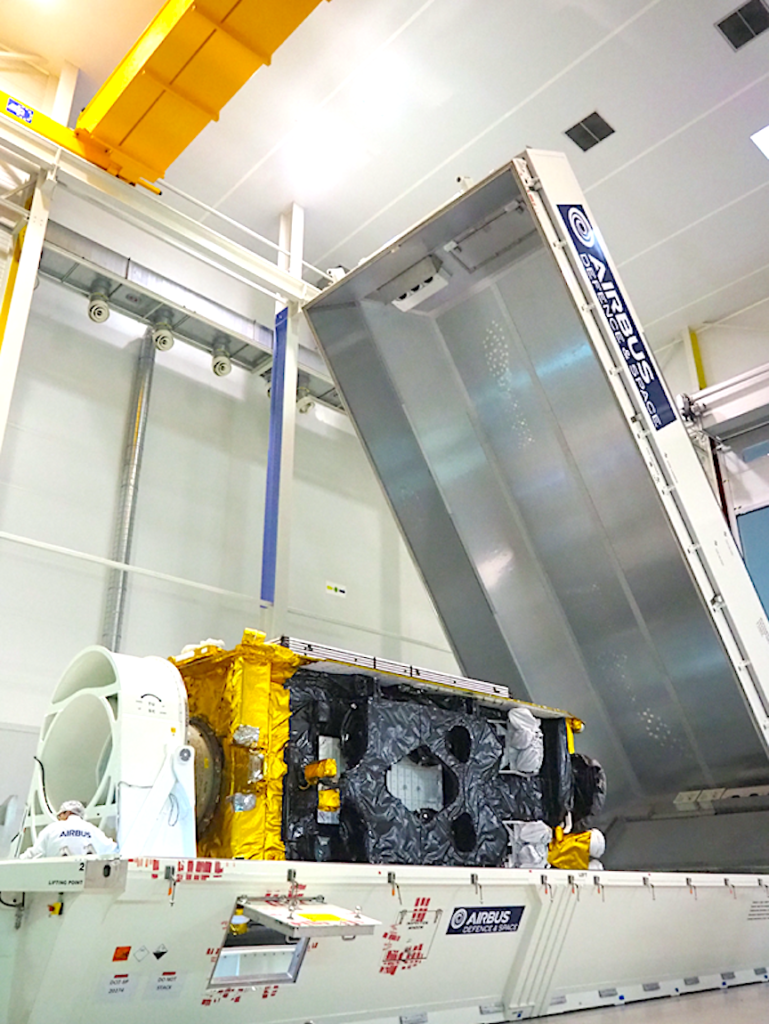
The second Airbus-built Inmarsat-6 geostationary telecommunications satellite (I-6 F2) has arrived on board an Airbus Beluga at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida ready for its launch in February.
The second satellite of the Inmarsat-6 generation is based on Airbus’ Eurostar E3000 spacecraft and will be the 58th Eurostar E3000 built by Airbus. It will be the ninth Eurostar in orbit that is equipped with electric propulsion for orbit raising, reinforcing Airbus’ position as the world leader in electric propulsion.

François Gaullier, Head of Telecommunications & Navigation Systems at Airbus, said, “I-6 F2, with its sophisticated digitally processed payload, will join Inmarsat-6 F1 (I-6 F1) in orbit giving Inmarsat even more flexibility, capability and capacity. This is the 10th geo-telecommunications satellite we have built for our long-term customer Inmarsat, a leading provider of global mobile satellite communication services, and with I-6 F1 the satellites will enable a step change in the capabilities and capacity for their ELERA services, and deliver significant additional capacity for their Global Xpress network.”
I-6 F1 and I-6 F2 each feature a large 9m aperture L-band antenna and six multi-beam Ka-band antennas, giving a high level of flexibility and connectivity. They also carry new generation modular digital processors to provide full routing flexibility over up to 8000 channels and dynamic power allocation to over 200 spot beams in L-band, per spacecraft. The Ka-band spot beams are steerable over the full Earth disk, with flexible channel to beam allocation.

The satellites will enable Inmarsat to further enhance its world-leading ELERA (L-band) and Global Xpress (Ka-band) networks respectively, for customers across land, sea, and air. They are also the next step in the company’s plans for the world’s first multi-dimensional network, Inmarsat ORCHESTRA. The ‘network of networks’ will build on Inmarsat’s existing space-based capabilities to provide a transformational growth in capacity and new features for customers into the 2030s and beyond.
Investments made by Airbus in platform and payload technologies used on I-6 are supported by the European Space Agency and national agencies, in particular the UK Space Agency and CNES, France’s National Centre for Space Studies. I-6 F2 has a launch mass of 5.5 tons, spacecraft power of 21 kW and a design life of more than 15 years.
The first Airbus built Inmarsat-6 (I-6 F1) satellite was successfully launched in December 2021. It reached its geostationary testing location in summer 2022 and is scheduled to enter service in early 2023. I-6 F2 is set to follow after its successful launch and enter service in early 2024.
Airbus’ geostationary telecommunications satellites have clocked up more than 1300 years of successful operation and are in service or being built for all of the world’s leading geostationary satellite operators.