
Image credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
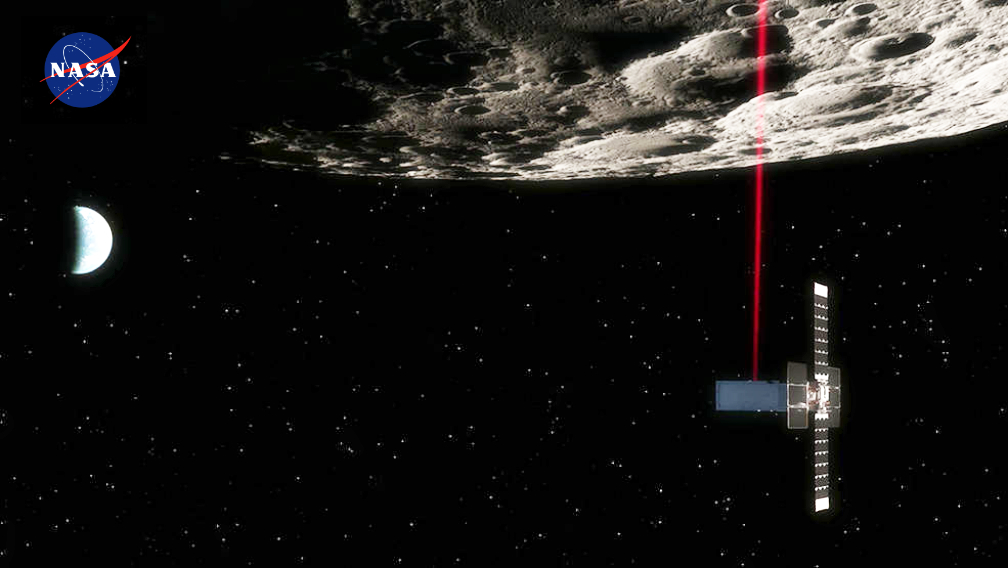
When NASA’s Lunar Flashlight launches, the smallsat will start a three month journey, with mission navigators guiding the spacecraft far past the Moon. The smallsat will then be slowly pulled back by gravity from Earth and the Sun before settling into a wide, science-gathering orbit to hunt for surface water ice inside dark regions on the Moon that haven’t seen sunlight in billions of years.
Photo credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
No larger than a briefcase, Lunar Flashlight will use a reflectometer equipped with four lasers that emit near-infrared light in wavelengths readily absorbed by surface water ice. This is the first time that multiple colored lasers will be used to seek out ice inside these dark craters.
Should the lasers hit bare rock or regolith (broken rock and dust), the light will reflect back to the spacecraft. But if the target absorbs the light, that would indicate the presence of water ice. The greater the absorption, the more ice there may be.
The spacecraft’s orbit – called a Near-Rectilinear Halo Orbit (NRHO) – will take it 43,000 miles (70,000 kilometers) from the Moon at its most distant point; at its closest approach, the satellite will graze the surface of the Moon, coming within 9 miles (15 kilometers) above the lunar South Pole.
Smallsats carry a limited amount of propellant, so fuel-intensive orbits aren’t possible. A near-rectilinear halo orbit requires far less fuel than traditional orbits and Lunar Flashlight will be only the second NASA mission to use this type of trajectory. The first is NASA’s Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) mission, which arrived at its orbit on November 13th., making its closest pass over the Moon’s North Pole.
Lunar Flashlight will use a new kind of “green” propellant that is safer to transport and store than the commonly used in-space propellants such as hydrazine. In fact, Lunar Flashlight will be the first interplanetary spacecraft to use this propellant — one of the mission’s primary goals is to test this technology for future use. The propellant was successfully tested on a previous NASA technology demonstration mission in Earth orbit.
The science data collected by Lunar Flashlight will be compared with observations made by other lunar missions to help reveal the distribution of surface water ice on the Moon for potential use by future astronauts.
“We are bringing a literal flashlight to the Moon – shining lasers into these dark craters to look for definitive signs of water ice covering the upper layer of lunar regolith,” said Barbara Cohen, Lunar Flashlight principal investigator at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “I’m excited to see our mission contribute to our scientific understanding of where water ice is on the Moon and how it got to be there.”
Lunar Flashlight is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on December 1st — see this SatNews posting…
