
The agency’s mission to explore Jupiter’s icy moon takes a big step forward as engineers deliver a major component of the spacecraft.

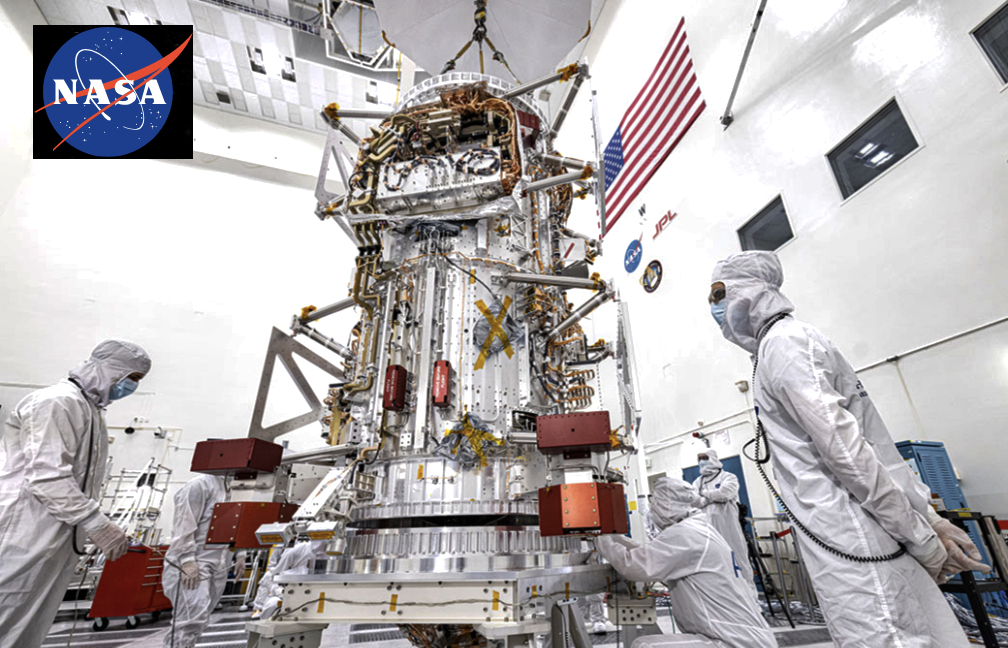
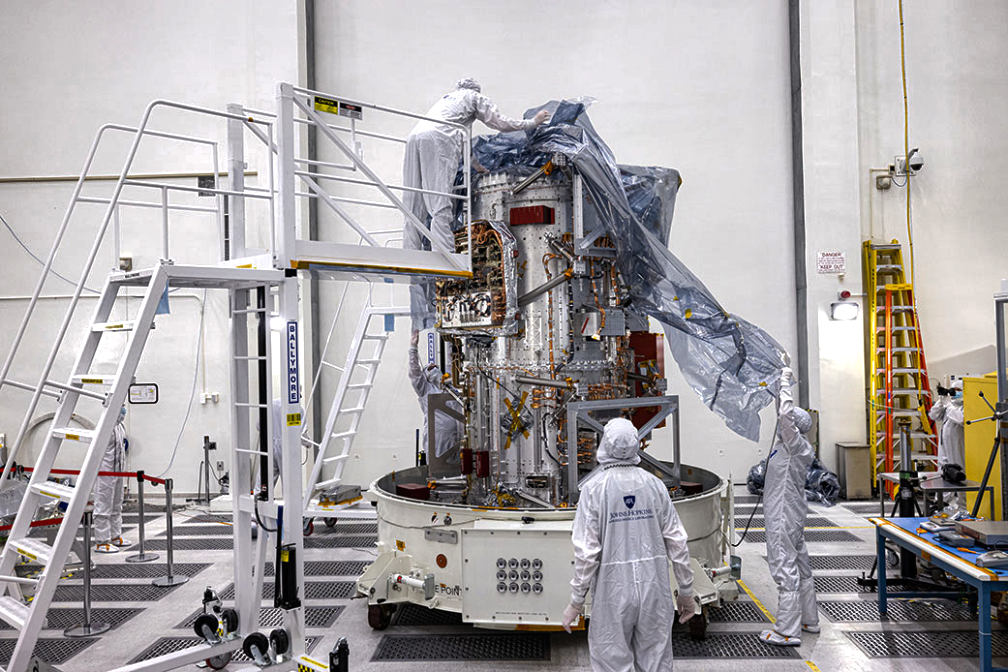
The main body of NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft has been delivered to the agency’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Over the next two years there, engineers and technicians will finish assembling the craft by hand before testing it to make sure it can withstand the journey to Jupiter’s icy moon Europa.

The spacecraft body is the mission’s workhorse. Standing 10 feet (3 meters) tall and 5 feet (1.5 meters) wide, it’s an aluminum cylinder integrated with electronics, radios, thermal loop tubing, cabling, and the propulsion system. With its solar arrays and other deployable equipment stowed for launch, Europa Clipper will be as large as an SUV; when extended, the solar arrays make the craft the size of a basketball court. This is the largest NASA spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission.
“It’s an exciting time for the whole project team and a huge milestone,” said Jordan Evans, the mission’s project manager at JPL. “This delivery brings us one step closer to launch and the Europa Clipper science investigation.”

Set to launch in October 2024, Europa Clipper will conduct nearly 50 flybys of Europa, which scientists are confident harbors an internal ocean containing twice as much water as Earth’s oceans combined. Plus, the ocean may currently have conditions suitable for supporting life. The spacecraft’s nine science instruments will gather data on Europa’s atmosphere, surface, and interior – information that scientists will use to gauge the depth and salinity of the ocean, the thickness of the ice crust, and potential plumes that may be venting subsurface water into space.
Those instruments already have begun arriving at JPL, where the phase known as assembly, test, and launch operations has been underway since March. The ultraviolet spectrograph, called Europa-UVS, arrived in March. Next came the spacecraft’s thermal emission imaging instrument, E-THEMIS, delivered by the scientists and engineers leading its development at Arizona State University. E-THEMIS is a sophisticated infrared camera designed to map Europa’s temperatures and help scientists find clues about the moon’s geological activity – including regions where liquid water may be near the surface.
By the end of 2022, most of the flight hardware and the remainder of the science instruments are expected to be complete.
The Entire Package
The Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, designed Europa Clipper’s body in collaboration with JPL and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
“The flight system designed, built, and tested by APL – using a team of hundreds of engineers and technicians – was the physically largest system ever built by APL,” said APL’s Tom Magner, the mission’s assistant project manager.
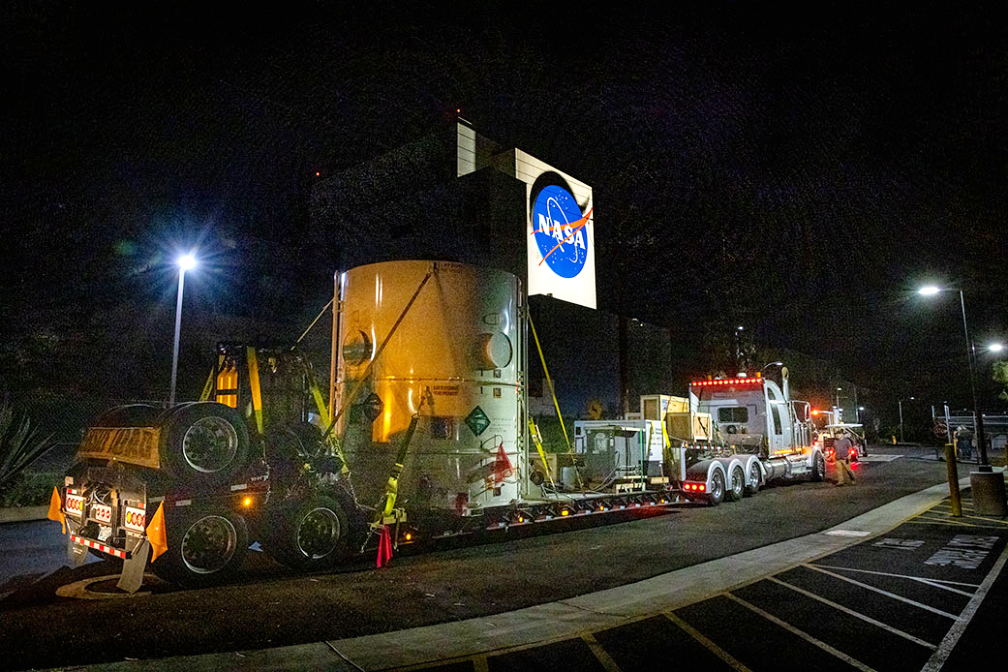

The work on the main module continues now at JPL.
“What arrived at JPL represents essentially an assembly phase unto itself. Under APL’s leadership, this delivery includes work by that institution and two NASA centers. Now the team will take the system to an even higher level of integration,” said Evans.
The main structure is actually two stacked aluminum cylinders dotted with threaded holes for bolting on the spacecraft’s cargo: the radio frequency module, radiation monitors, propulsion electronics, power converters, and wiring. The radio frequency subsystem will power eight antennas, including an enormous high-gain antenna that measures 10 feet (3 meters) wide. The structure’s web of electrical wires and connectors, called the harness, weighs 150 pounds (68 kilograms) by itself; if stretched out, it would run almost 2,100 feet (640 meters) – twice the perimeter of a football field.
The heavy-duty electronics vault, built to withstand the intense radiation of the Jupiter system, will be integrated with the main spacecraft structure along with the science instruments.
Inside the main body of the spacecraft are two tanks – one to hold fuel, one for oxidizer – and the tubing that will carry their contents to an array of 24 engines, where they will combine to create a controlled chemical reaction that produces thrust.
“Our engines are dual purpose,” said JPL’s Tim Larson, the deputy project manager. “We use them for big maneuvers, including when we approach Jupiter and need a large burn to be captured in Jupiter’s orbit. But they’re also designed for smaller maneuvers to manage the attitude of the spacecraft and to fine tune the precision flybys of Europa and other solar system bodies along the way.”
Those big and small maneuvers will come into play a lot during the six-year, 1.8-billion-mile (2.9-billion-kilometer) journey to this ocean world, which Europa Clipper will begin investigating in earnest in 2031.
More About the Mission
Missions such as Europa Clipper contribute to the field of astrobiology, the interdisciplinary research on the variables and conditions of distant worlds that could harbor life as we know it. While Europa Clipper is not a life-detection mission, it will conduct detailed reconnaissance of Europa and investigate whether the icy moon, with its subsurface ocean, has the capability to support life. Understanding Europa’s habitability will help scientists better understand how life developed on Earth and the potential for finding life beyond our planet.
Managed by Caltech in Pasadena, California, JPL leads the development of the Europa Clipper mission in partnership with APL for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, executes program management of the Europa Clipper mission.
