
The U.S. Space Force has awarded Launcher Space $1.7 million to further develop the company’s E-2 engine, which was proven earlier this month at NASA Stennis Space Center to be the highest-performing liquid oxygen and kerosene rocket engine combustion chamber in the U.S.

The U. S. Space Force’s support advances E-2 development and helps to meet the goals of the Department of Defense (DoD) by maximizing performance and payload capacity for a small launch vehicle, accelerating vehicle production and removing geographic and supply chain constraints for volume production.
In the words of the U.S. Space Force, “Launcher’s high performance engine design materially increases a rocket’s payload capacity by consuming less propellant while generating the same thrust. As a result, Launcher’s E-2 liquid rocket engine also has the potential to significantly reduce the price to deliver small satellites to orbit on dedicated small launch vehicles, which is a key capability and priority for the Space Force.” – U.S. Space Force Memorandum, June 2021

Launcher E-2 is a closed cycle, 3D-printed, high-performance, liquid rocket engine in development for the Launcher Light launch vehicle, scheduled to fly in 2024. A single E-2 engine will boost Launcher Light to LEO with 150 kg. of payload. Launcher’s achievements:
- Demonstrated the highest performance of any small launch vehicle in development worldwide
- Demonstrated the highest performance of a liquid oxygen & kerosene liquid rocket engine combustion chamber in the U.S.
- Demonstrated the second highest performance of a kerosene liquid rocket engine of any size, globally
The combination of these five key design decisions makes Launcher’s high-performance possible:
- 3D-printing single-piece copper alloy combustion chamber
- Use of copper alloy and liquid oxygen regenerative cooling, removing the need for film cooling of any kind on the injector or combustion chamber
- Higher combustion pressure than any small launch vehicle engine, active or in development
- State-of-the-art coaxial swirl injector, bringing combustion efficiency above 97.5%
- Oxygen-rich closed-cycle engine, removing the need for extra propellant to be used for turbopump power as required by open-cycle engines
Test data evidence from one of the May 4, 2022 E-2 test fire at NASA Stennis Space Center:
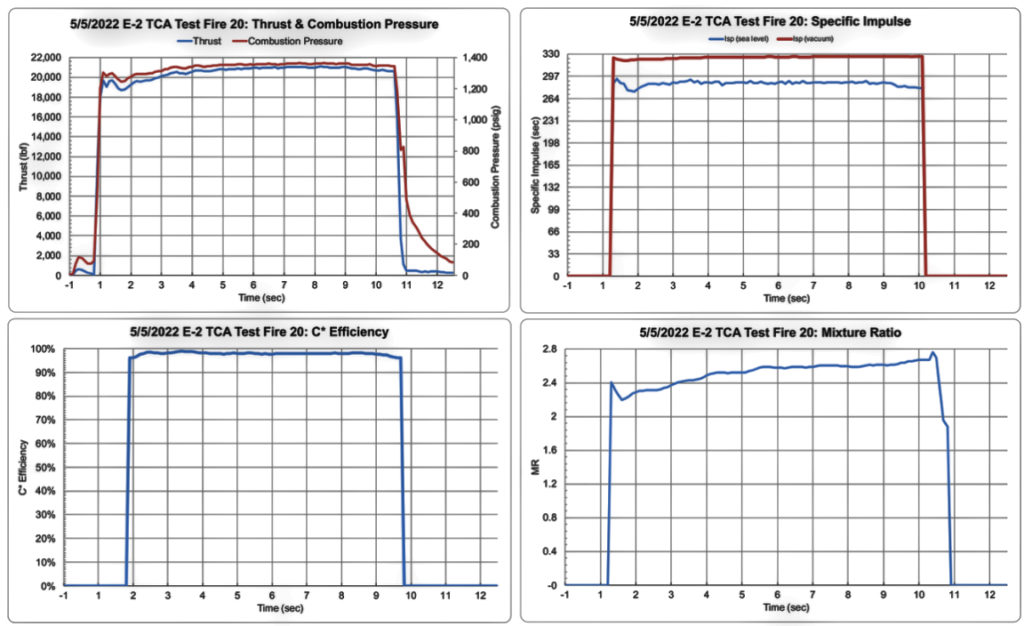
The only possible means of material performance improvement is to increase combustion pressure. Despite the fact that we already beat the performance of every small launch vehicle in development, worldwide, we plan to do so in future engines. All other criteria, such as mixture ratios and combustion efficiency, are already near or at the theoretical maximum. Lower cost aviation kerosene compatibility enables lower prices for the U.S. military and other customers.
In its successful test-fire campaign, Launcher also demonstrated the E-2 engine with Jet-A aviation kerosene and rocket grade kerosene (RP-1). The company proved full functionality and similar performance using the lower cost, easier-to-source aviation Jet-A fuel. Demonstrating Jet-A fuel compatibility meets an important goal of the U.S. Space Force’s responsive launch strategy requirements. Standard Copper Alloy reduces supply chain constraints and dependencies.
Launcher’s E-2 engine is 3D-printed in a standard industrial copper alloy (CuCrZr or C18150) that has the advantage of being low cost and readily available through a strong global supply chain when compared to specialized copper alloy optimized for rocket engines.
The USSF award on May 18, 2022, will provide Launcher with additional funding to advance and accelerate the development of Launcher’s E-2 engine including:
