
Orbit Logic has been awarded a Phase II Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) contract by NASA to further mature the Intelligent Navigation, Planning, and Awareness for Swarm Systems (IN-PASS) solution.
IN-PASS builds on Orbit Logic’s flight-proven Autonomous Planning System (APS) decentralized planning framework to enable the configuration, evaluation and validation of team-collaborative, robotic mission concepts. IN-PASS is being developed in partnership with the University of Colorado Boulder (CU).
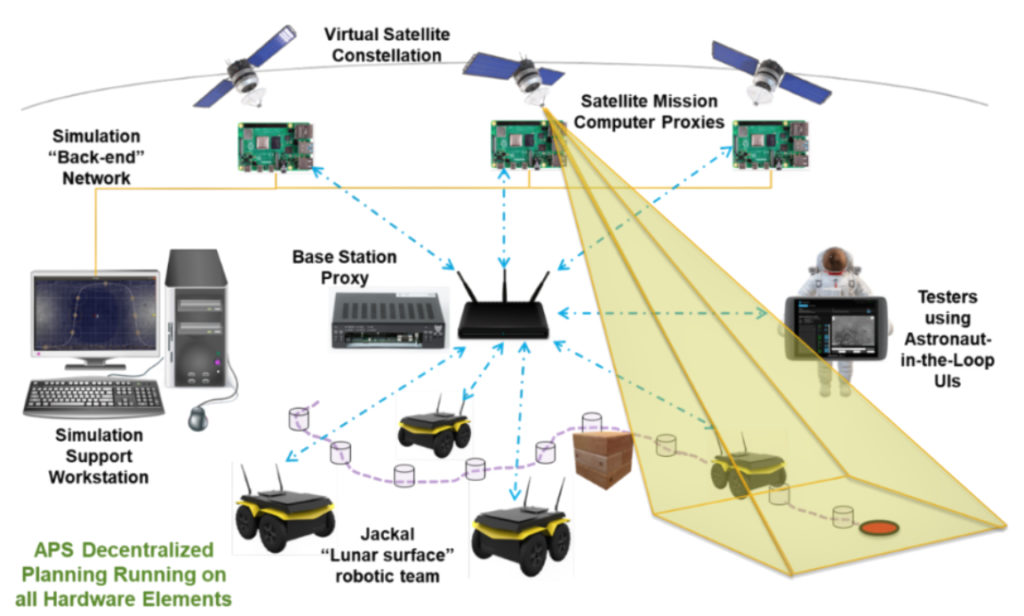
Phase II efforts will focus on the build-out of a mixed-mode testbed in CU’s Autonomous Systems Programming Evaluating and Networking (ASPEN) laboratory, where the satellite assets will be simulated (running their software on proxy flight computing elements) but use live, COTS, robotic rovers for the surface team. APS instances on each swarm asset will facilitate team-level coordination through decentralized mission planning approaches.
Event-Triggered Decentralized Data Fusion (ET-DDF) will be used to maintain a common view of team states across intermittent and time-varying communication networks using minimal information exchange. A formal methods approach to onboard planning will be employed on the rover assets, using a Markov Decision Process (MDP) to balance performance, resource usage and safety.
In a sample mission, APS on the satellites will plan sensor collections in support of multiple objectives (surface asset localization and surface chemistry detection), then plan and orchestrate the delivery of data products to a surface asset with high processing capacity, where algorithms will be invoked to identify the locations of rovers and areas of science interest (AOIs). Resulting rover location measurements could enhance ET-DDF’s ability to maintain shared team awareness – critical to the team’s ability to autonomously coordinate. AOI events are triggers for rovers to plan their navigation to the contact science locations using the MDP algorithms.
Astronauts could participate in-the-loop with these swarms using devices running interactive user interfaces that would allow them to a) specify mission goals, b) receive feedback on the satisfaction of their requests as the team performs the associated tasks, c) receive and display the end data associated with their requests, and d) actually collaborate with the autonomous robots by electing to assume tasks they are well suited to perform.
Orbit Logic Chief Operating Officer Ella Herz said, “It’s great to see APS being used for multi-domain operations optimization and autonomy – the example scenario is for the Moon, but this could be used on Earth as well for firefighting, military operations and more. The way IN-PASS coordinates assets while taking into account power and communications limitations is particularly impressive.”
