
Rocket Lab USA, Inc (Nasdaq: RKLB) has revealed new details about their next generation Neutron launch vehicle.

This advanced, 8-ton, payload class Neutron launch vehicle is designed to transform space access by delivering reliable and cost-effective launch services for satellite mega-constellations, deep space missions and human spaceflight. During a live streamed Neutron update, Rocket Lab founder and CEO Peter Beck revealed new details about Neutron’s unique design, materials, propulsion, and reusability architecture for the first time.

Neutron will be the world’s first carbon composite large launch vehicle. Rocket Lab pioneered the use of carbon composite for orbital rockets with the Electron rocket, which has been delivering frequent and reliable access to space for government and commercial smallsats since 2018. Neutron’s structure will be comprised of a new, specially formulated carbon composite material that is lightweight, strong and can withstand the immense heat and forces of launch and re-entry again and again to enable frequent re-flight of the first stage. To enable rapid manufacturability, Neutron’s carbon composite structure will be made using an automated fiber placement system which can build meters of carbon rocket shell in minutes.
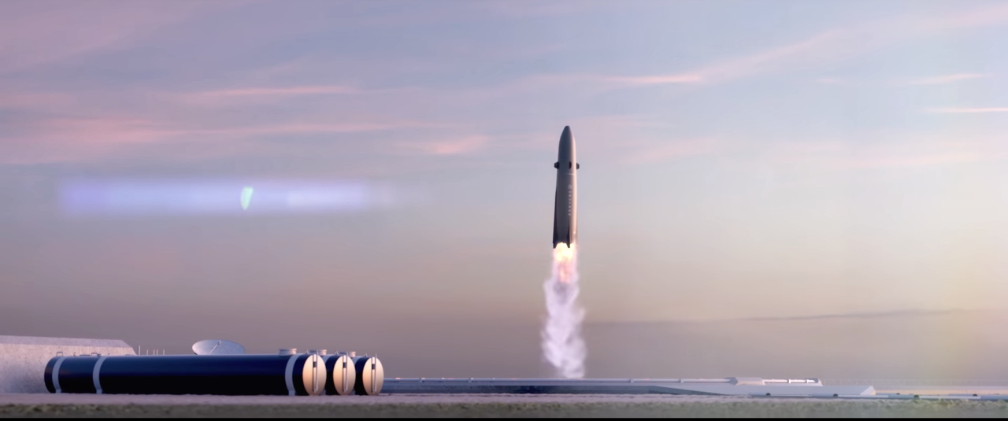
Reusability is key to enabling frequent and affordable launch, so the ability to launch, land and lift-off again has been built into every aspect of Neutron’s design from day one. It starts with Neutron’s unique shape, a tapered rocket with a wide base to provide a robust, stable base for landing, eliminating the need for complex mechanisms and landing legs. This balanced structure also removes the need for bulky launch site infrastructure, including strongbacks and launch towers. Neutron will, instead, stand securely on its own legs for lift-off. After reaching space and deploying Neutron’s second stage, the first stage will return to Earth for a propulsive landing at the launch site, eliminating the high costs associated with ocean-based landing platforms and operations.

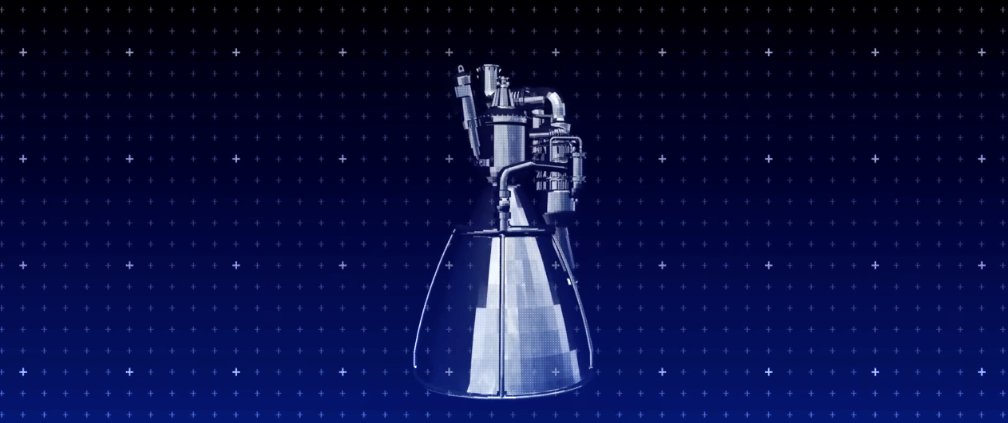
Neutron will be powered by an entirely new rocket engine, Archimedes. Designed and manufactured in-house by Rocket Lab, Archimedes is a reusable liquid oxygen / methane gas generator cycle engine capable of 1 meganewton thrust and 320 seconds of ISP. Seven Archimedes engines will propel Neutron’s first stage, with a single vacuum optimized Archimedes engine on the second stage. Neutron’s lightweight carbon composite structure means Archimedes does not need the immense performance and complexity typically associated with larger rockets and their propulsion systems. By developing a simple engine with modest performance requirements, the timeline for development and testing can be drastically accelerated.

What makes Neutron’s design especially unique is the captive ‘Hungry Hippo’ fairing design. This innovative design will see the fairing form part of the first stage structure and remain fixed to the stage. Rather than separating from the stage and falling away to the ocean like traditional fairings, Neutron’s Hungry Hippo fairing jaws will open wide to release the second stage and payload, before closing again ready to return to Earth with the first stage. What lands back on the launch pad is a compete first stage with fairings attached, ready for a new second stage to be integrated and launched. This advanced design can speed up launch frequency, eliminates the high cost, low reliability method of capturing fairings at sea, and enables the second stage to be lightweight and nimble.
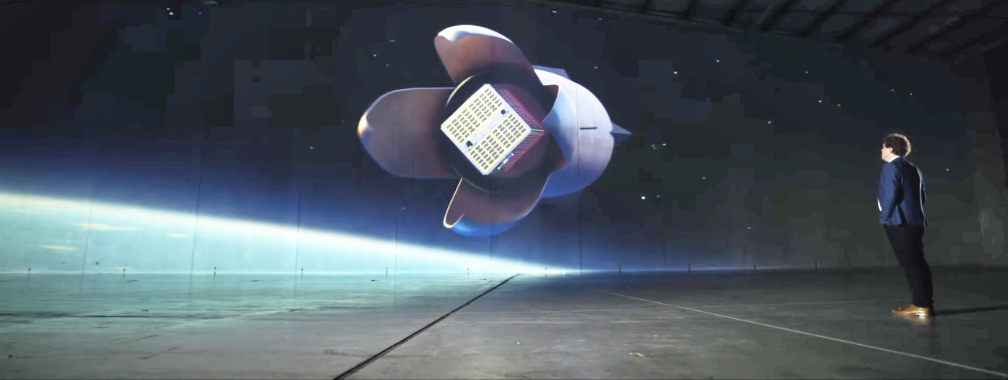
Thanks to Neutron’s ‘Hungry Hippo’ fairing design, the entire second stage will be completely enveloped within the Neutron’s first stage structure and fairing during launch. Thanks to this, Neutron’s second stage is designed to be the lightest in history to enable high performance for complex satellite deployments. Typically, a second stage forms part of the launch vehicle’s exterior structure and needs to provide strength to the vehicle from lift-off, exposing it to the harsh environments of the lower atmosphere during launch.
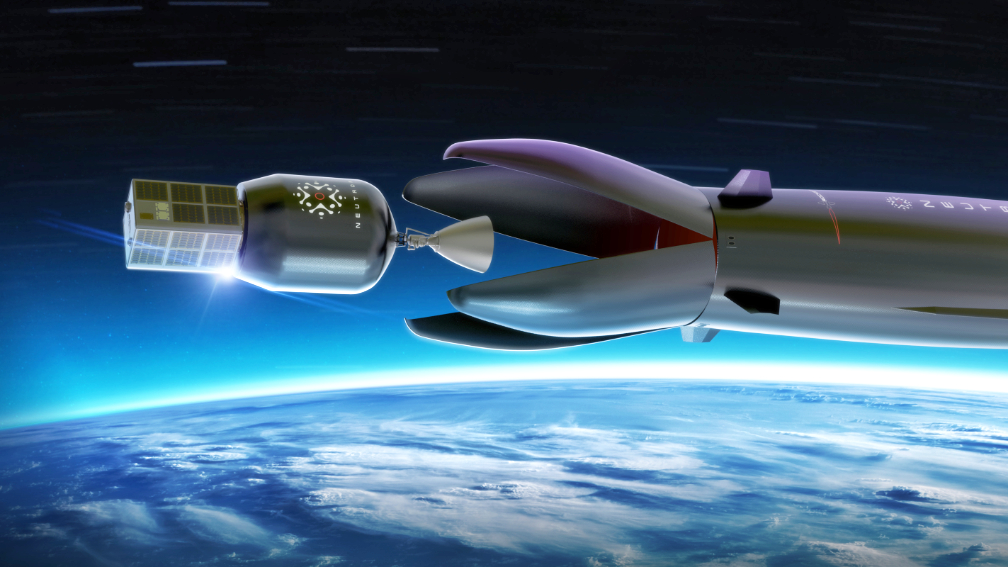
By being housed inside the first stage and ‘Hungry Hippo’ fairing, the requirement for the second stage to withstand the launch environment is eliminated and the second stage can be made significantly lighter enabling higher performance in space. Designed as an expendable upper stage for now, Neutron’s second stage is a six-meter-long carbon composite structure with a single vacuum optimized Archimedes engine.

Rocket Lab is currently working through a competitive process to select launch site, rocket production facility and Archimedes engine test facility on the U.S. East Coast. Rocket Lab expects to create around 250 new jobs to support the Neutron program with many roles open for application now.
“Neutron is not a conventional rocket. It’s a new breed of launch vehicle with reliability, reusability and cost reduction is hard baked into the advanced design from day one. Neutron incorporates the best innovations of the past and marries them with cutting edge technology and materials to deliver a rocket for the future,” said Mr. Beck. “More than 80% of the satellites to be launched in the next decade are expected to be constellations, which have unique deployment needs that Neutron is the first vehicle to address specifically. Like we did with Electron, rather than starting with a traditional rocket design, we focused on our customers’ needs and worked back from there. The result is a rocket that is right-sized for market demand and can launch fast, frequently and affordably.”
Note: All imagery is courtesy of Rocket Lab.
