Lana Narine, an assistant professor of geospatial analytics in the Auburn University School of Forestry and Wildlife Sciences, is part of a research team whose recent study presented a breakthrough in the capabilities of a NASA satellite to examine the three-dimensional structure of forests.
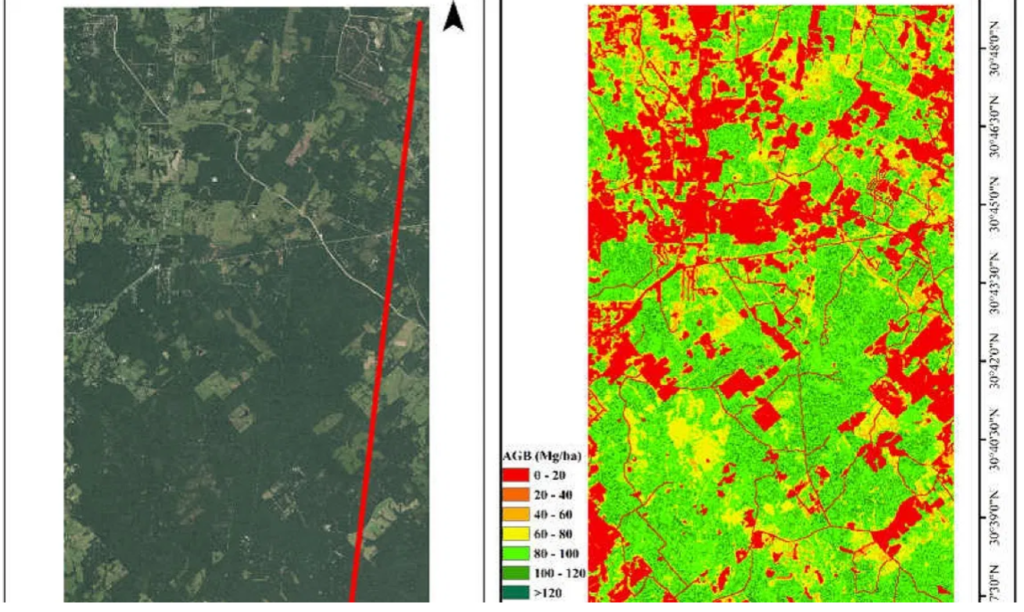
The study, “Using ICESat-2 to Estimate and Map Forest Aboveground Biomass: A First Example” in the journal Remote Sensing, shows how NASA’s Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2, or ICESat-2, can be used to estimate aboveground biomass, or AGB, of forests and map its distribution.
Narine said limited information on the three-dimensional structure of forests has contributed to uncertainties in determining carbon budgets. However, ICESat-2 can capture this information using a laser-based lidar (light detection and ranging) instrument.

Lidar facilitates direct three-dimensional structural measurements, and using this technology from a space-based platform translates to exciting possibilities for assessing forest resources up to global scales, Narine said.
Knowing the capabilities of ICESat-2 allows for a better understanding of the satellite’s capabilities and limitations for characterizing vegetation.
“With ICESat-2 providing elevation measurements globally, a plethora of indicators of ecosystem health and function — including a key surrogate measure of forest AGB — can be potentially estimated to support sustainable management of forests,” Narine said.
The ICESat-2 mission was primarily designed to capture ice measurements, but its capture of data over vegetated areas offers investigators broader insights into ecosystem structure and the potential to contribute to the sustainable management of forest ecosystems.
Narine’s research implemented methods she worked on prior to the start of the mission to better understand the data and to develop methodologies for vegetation applications.
Janaki Alavalapati, dean of the School of Forestry and Wildlife Sciences, said the study is groundbreaking in its field.
“Dr. Narine’s role in researching the capabilities of the NASA Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 is yet another notable contribution from our faculty in the rapidly evolving field of geospatial and environmental informatics,” Alavalapati said. “This study has provided the first example of the satellite’s unique ability to gather critical data from forests that was previously unavailable.”
Narine’s co-authors were Sorin C. Popescu and Lonesome Malambo of the Department of Ecology and Conservation Biology at Texas A&M University, Narine’s former institution. Narine is a co-investigator on a NASA grant with the same team, with Popescu as principal investigator.
By Teri Greene, Auburn University
This story originally appeared on Auburn University’s website.