The good news is that procurements with these innovative propulsion companies demonstrates a vigorous U.S. industrial base, with small businesses leading the way…
Astrobotic’s Griffin Mission One (GM1) team selected Agile Space Industries for Attitude Control System (ACS) thrusters and Frontier Aerospace for axial engines for their Griffin lunar lander. Astrobotic’s Griffin will deliver NASA’s Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the South Pole of the Moon in late 2023. Upon landing, VIPER will map the presence of water ice on the Moon.
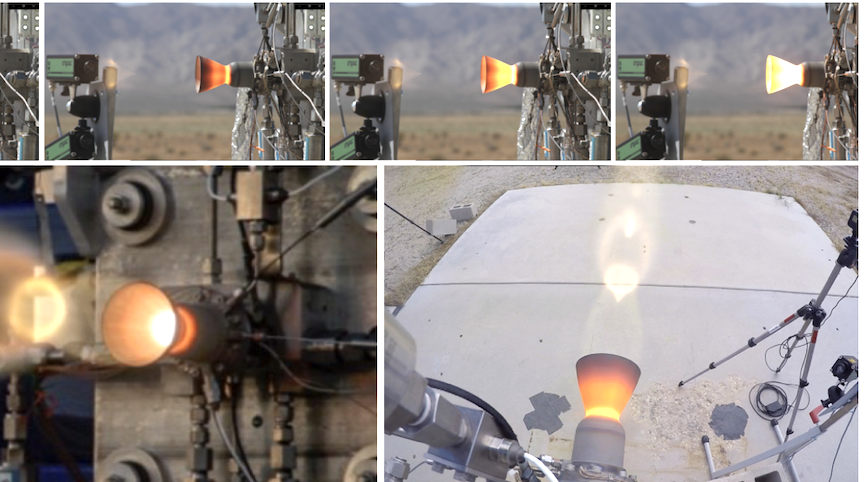
Agile was selected as the ACS thrusters provider for Griffin and will deliver twelve flight thrusters, in addition to building spare and fit check thrusters. Agile successfully performed the first in a series of hot fire tests in January 2021, using their test cell to simulate the vacuum and harsh conditions of space. Delivery of flight thrusters is expected in 2022.
Daniel Gillies, Astrobotic’s GM1 Mission Director said, “By utilizing rapid prototyping techniques and an in-house test capability, Agile has moved quickly from concept to functional hot firing of the ACS thrusters that allow Astrobotic to obtain performance data earlier than traditional methods would allow. This represents months of additional schedule margin for GM1.”
Frontier Aerospace brings the legacy of its F500E engine design to the Griffin lander in delivery of five 700-lbf engines. These engines will be used to brake Griffin into lunar orbit and safely descend to a soft touchdown on the lunar surface. The flight engines for Griffin will be delivered in 2022, with the first hot fire tests scheduled for the coming months.
“Frontier Aerospace brings a wealth of knowledge in bi-propellent engine design and a proven foundation from their F500 series of engines. We’ve entrusted Frontier’s engines to perform the most critical propulsive maneuvers on GM1, building on our successful relationship from our first Peregrine mission,” says Gillies.
In addition to making propulsion acquisitions, Astrobotic also completed major milestones in the GM1 program through the completion of the System Requirements Review (SRR) and the procurement of a number of other long lead components. At the SRR, Astrobotic reviewed the NASA Payload, Mission, and Lander requirements against the system design. Given that many of the elements of Griffin have a foundation in Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander set to launch later in 2021, a large part of the review involves confirming these subsystem requirements meet VIPER-specific mission requirements. Many of Griffin’s components are similar to those in Peregrine, but a full analysis of requirements was vital for success.
Astrobotic marked another major milestone for GM1 at the turn of the new year with procurement of forgings that form Griffin’s primary structure. These forgings will eventually be machined into final parts that make up both the interface to the launch vehicle and to VIPER for both the structural test model and flight article of Griffin.
A launch vehicle for the Griffin lunar lander is set to be chosen soon. Assembly of Griffin’s flight equivalent Structural Test Model (STM) will commence in Q3 of 2021 at Astrobotic’s headquarters in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Qualification testing is scheduled to be completed before the end of the year.

