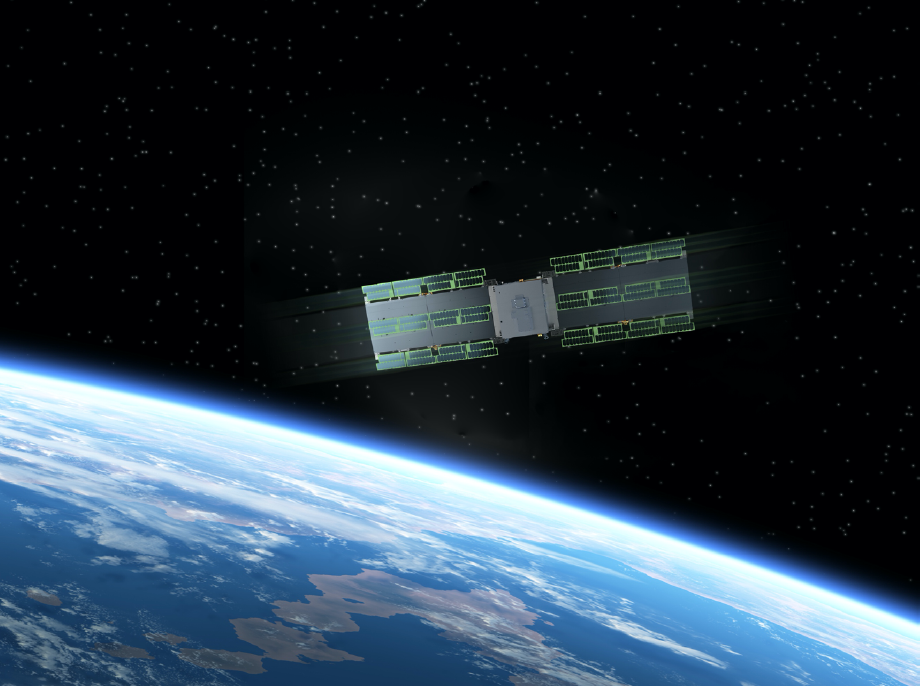
ThrustMe and Spacety have announced a new space launch, the 3rd in an ongoing series — this time, Spacety launched their Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellite, Hisea-1, which is the world’s first, commercial, C-band, smallsat SAR with a phased array antenna.
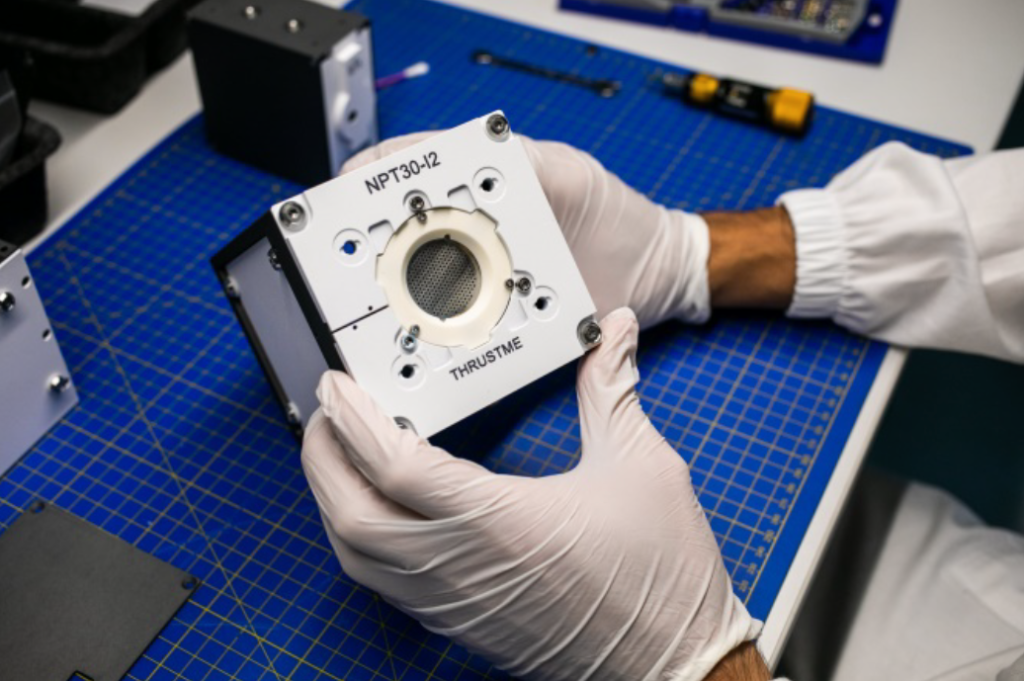
On board is ThrustMe’s Iodine Electric Propulsion system to provide the satellite with crucial orbit maintenance, collision avoidance and de-orbiting at the end of its three years expected lifetime. The satellite was successfully launched into space on the inaugural flight of the Chinese medium-lift Long March 8 rocket, from Wenchang, China.

Hisea-1 has a mass of 180 kg, and uses a phased-array antenna. It has three imaging modes with its finest resolution at 1m x 1m.
Hisea-1 was launched to meet the needs for the monitoring of ocean and coastal areas and for ocean research. The imagery from the satellite will also be used for disaster management, agriculture, infrastructure monitoring, etc.
Synthetic Aperture Radars (SAR) functions basically like a bat’s echolocation system — they are much less effected by daylight and weather conditions compared to optical sensors. Now the era of SAR satellites has come, and Spacety is planning a constellation of 56 smallsats.
Spacety and ThrustMe announced just a month ago the launch of the first iodine electric propulsion on-orbit-demonstrations missions, which has successfully completed the commissioning phase, and the longer thruster firings will take place soon. For ThrustMe, the technology demonstration phase is now transitioning into entering the commercial market where Spacety is one of their early adopter clients. Streamlined and true turnkey propulsion is more important than ever before. As Euroconsult announced recently, there will be, on average, 1,200 satellites launched per year over the next decade.
“Hisea-1 is the first launched satellite of TY-MINISAR, the first generation of light and small SAR satellites being developed by Spacety. The constellation based on TY-MINISAR benefits from low cost, fast deployment, strong coverage capability, and flexible scheduling. As a result, the constellation can produce images of high resolution with a high revisit frequency, wide-coverage, and with continuous monitoring, and providing customers with more efficient remote sensing services,” said Justin Feng, the Founder and CEO of Spacety.
“As for most miniaturized SAR satellites operating in Low-Earth-Orbit (LEO), the orbital precision will drive the quality of the data we receive. Therefore ThrustMe’s iodine electric propulsion will be a crucial sub-system to ensure our mission’s success,” noted Ren Weijia, CTO of Spacety.
“We have worked with Spacety for over one and a half years now, testing step by step our unique propulsion solutions in space, and as a result we can now deliver true turnkey and streamlined propulsion systems to Spacety in time for their SAR constellation deployment,” added time for their SAR constellation deployment,” added Ane Aanesland, the CEO of ThrustMe.
“Because of the exponential growth in the number of satellites launched into LEO and MEO orbits, every actor needs to take responsibility, and having on-board propulsion is the only way we can ensure that our satellites can perform collision avoidance if needed, and can de-orbit at the end of life,” said Jame Zheng, CEO of Spacety Luxembourg, who stressed the importance of sustainable actions before it is too late to do so.