Lockheed Martin will manage, build and operate the spacecraft.
The University of Colorado Boulder and Lockheed Martin (NYSE: LMT) will soon lead a new space mission to capture the first-ever closeup look at a mysterious class of solar system objects: binary asteroids.
These bodies are pairs of asteroids that orbit around each other in space, much like the Earth and Moon. In a project review on September 3, NASA gave the official go-ahead to the Janus mission, named after the two-faced Roman god.
The mission will study these asteroid couplets in never-before-seen detail. Known as Key Decision Point-C (KDP-C), this review and approval from NASA allows for the project to begin implementation, and baselines +the project’s official schedule and budget.
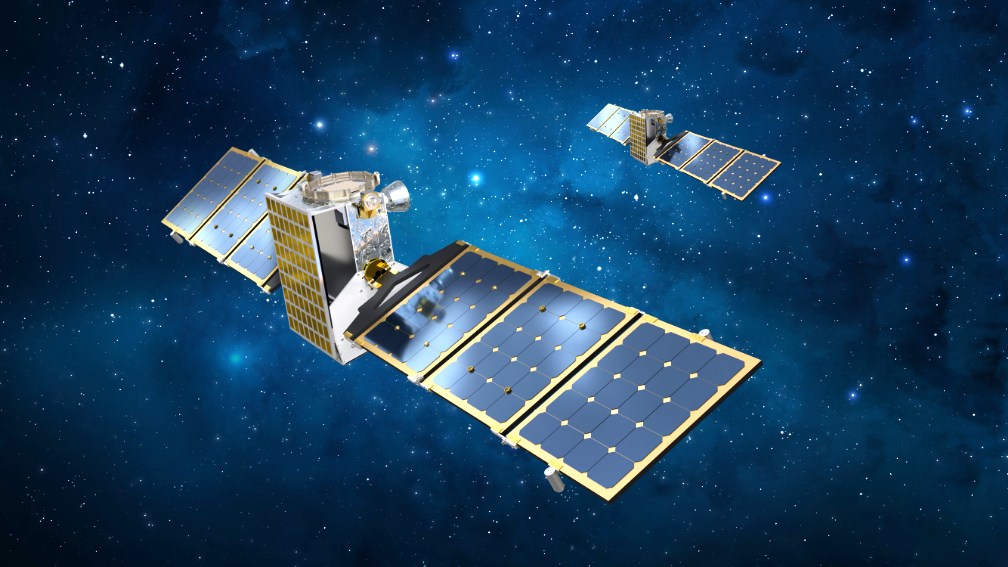
It will be a moment for twos: In 2022, the Janus team will launch two identical spacecraft that will travel millions of miles to individually fly close to two pairs of binary asteroids. Their observations could open up a new window into how these diverse bodies evolve and even burst apart over time, said Daniel Scheeres, the principle investigator for Janus.
The mission, which will cost less than $55 million under NASA’s SIMPLEx program, may also help to usher in a new era of space exploration, said Lockheed Martin’s Janus Project Manager Josh Wood. He explained that Janus’ twin spacecraft are designed to be small and nimble, each one about the size of a carry-on suitcase. After blasting off in 2022, the smallsats will first complete an orbit around the sun before heading back toward Earth and sling-shotting their way far into space and beyond the orbit of Mars.

Janus is led by the University of Colorado Boulder, where Scheeres is based, which will also undertake the scientific analysis of images and data for the mission. Lockheed Martin will manage, build and operate the spacecraft.
The mission will rendezvous with two binary pairs—named 1996 FG3 and 1991 VH—each showcasing a different kind of orbital pattern. The pair called 1991 VH, for example, has a “moon” that whips around a much bigger “primary” asteroid following a hard-to-predict pattern.
The team will use a suite of cameras to track the dynamical motion in unprecedented detail. Among other goals, Scheeres and his colleagues hope to learn more about how binary asteroids move—both around each other and through space.
Executive Comments

“Binary asteroids are one class of objects for which we don’t have high-resolution scientific data,” said Daniel Scheeres, distinguished professor in the Ann and H.J. Smead Department of Aerospace Engineering Sciences at CU Boulder. “Everything we have on them is based on ground observations, which don’t give you as much detail as being up close. Once we see them close up, there will be a lot of questions we can answer, but these will raise new questions as well. We think Janus will motivate additional missions to binary asteroids.”

“We see an advantage to be able to shrink our spacecraft,” said Josh Wood. “With technology advancements, we can now explore our solar system and address important science questions with smaller spacecraft.” Wood added that the mission’s twin spacecraft, each of which weigh just about 80 pounds, will travel farther than any smallsat to date. He added, “I think it’s a great test for what is achievable from the aerospace community,” Wood said. “And the Colorado-centric development for this mission, combining the space talent of both CU Boulder and Lockheed Martin, is a testament to the skills available in the state.”